Now-a-Days in Pakistan we hear the term 3G and 4G. basically these are the terms related to mobile communication and not only used in Pakistan but used in whole world. These terms related to Internet.
We must know that the Internet is a global network of networks. A group of interconnected users (via mobile / wireless), and sharing software and hardware resources between many users over the internet.
Now the question arise that; what is sharing and how it can be done?
Shering:
Basically shearing means that the shifting the information between one place to the another place which is done thrugh the communication.
Communications:
A system that enables users of telephones or data communications lines to exchange information over long distances by connecting with each other through a system of routers, servers, switches, and the like.
Now what are the terms 1G, 2G 3G, 4G AND LTE which are used in the world?
See the diagram :-
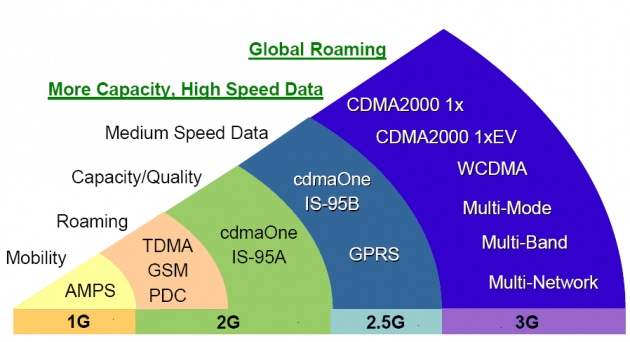
Now we will discuss the following:-
- 1G means 1st Generation Network
- 2G means 2nd Generation Network
- 3G means 3rd Generation Network
- 4G means 4th Generation Network
1G (1st Generation Network) :
We know that 1G or 1-G refers to the first generation and it is wireless telephone technology (mobile telecommunications). These are the analog telecommunications standards that were introduced in the 1980s and continued until being replaced by 2G digital telecommunications. 1G speeds vary from that of a 28k modem (28kbit/s) to a 56k modem (56kbit/s).
1G was an analog system, and was developed in the 70’s, 1G had two major improvements, this was the invention of the microprocessor, and the digital transform of the control link between the phone and the cell site.
2G (2nd Generation Network)
2G is 2nd generation network which is more advance from 1G. Three primary benefits of 2G networks over their predecessors were that phone conversations were digitally encrypted; 2G systems were significantly more efficient on the spectrum allowing for far greater mobile phone penetration levels; and 2G introduced data services for mobile, starting with SMS text messages. Second Generation wireless telephone technology (2G) were commercially launched on the GSM. The main difference between the two mobile telephone systems (1G and 2G), is that the radio signals used by 1G networks are analog, while 2G networks are digital. Digital voice data can be compressed and multiplexed much more effectively than analog voice encodings through the use of various codecs, allowing more calls to be transmitted in same amount of radio bandwidth.
Although both systems(1G & 2G) use digital signaling to connect the radio towers (which listen to the handsets) to the rest of the telephone system, the voice itself during a call is encoded to digital signals in 2G whereas 1G is only modulated to higher frequency, typically 150 MHz and up. GPRS (General Packet Radio Service), you have a theoretical transfer speed of max. 50 kbit/s (40 kbit/s in practice).
EDGE (Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution), you have a theoretical transfer speed of max. 250 kbit/s (150 kbit/s in practice).
3G (3rd Generation):
3G is a collection of third generation cellular data technologies. 3G technology is the result of research and development work carried out by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in the early 1980s. 3G specifications and standards were developed in fifteen years.
The first generation (1G) was introduced in 1982, while the second generation of cellular data technologies (2G) became standardized in the early 1990s. 3G technologies were introduced as early as 2001, but did not gain widespread use until 2007.
The communication spectrum between 400 MHz to 3 GHz was allocated for 3G.
While many cell phone companies market phones with "3G technology," there is no single 3G standard. Rather, different companies use their own technologies to achieve similar data transfer rates.
In India, 3G is defined by telecom service providers as minimum 2 Mbit/s to maximum 28 Mbit/s.
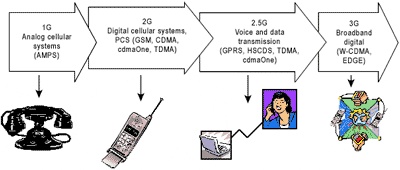
4G (4th Generation):
Fourth Generation of cellular data technologies, 3G precedes 4G. In addition to all the 3G facilities, data transmission is believed to go through the roof with speeds ranging between 100MBPs to 1GBPS.

All 4G standards must conform to a set of specifications created by the International Telecommunications Union. For example, all 4G technologies are required to provide peak data transfer rates of at least 100 Mbps. While actual download and upload speeds may vary based on signal strength and wireless interference. 4G data transfer rates can actually surpass those of cable modem and DSL connections.
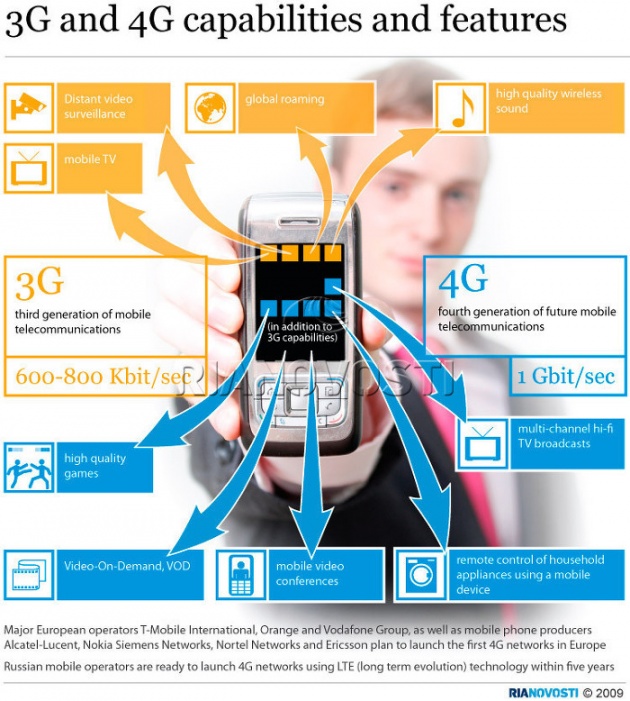
There is no single 4G standard like 3G. Instead, different cellular providers use different technologies that conform to the 4G requirements. For example, WiMAX is a popular 4G technology used in Asia and Eastern Europe, while LTE (Long Term Evolution) is more popular in United states.