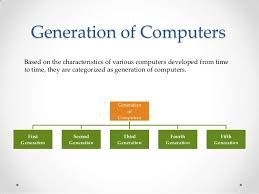
Generations Of Computer
Computer can be classified into following five generations
1st Generation Computers
2nd Generation Computers
3rd Generation Computers
4th Generation Computers
5th Generation Computers
1st Generation Computers:
During the period of 1940 to 1956 first generation of computers were developed. The first generation computers used vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory, and were often enormous, taking up entire rooms. The vacuum tube was developed by Lee DeForest. A vacuum tube is a device generally used to amplify a signal by controlling the movement of electrons in an evacuated space. First generation computers were very expensive to operate and in addition to using a great deal of electricity, generated a lot of heat, which was often the cause of malfunctions.
A View Of Vacuum Tube

CHARACTERISTICS:
1) First generation computers were based on vacuum tubes.
2) The operating systems of the first generation computers were very slow.
3) They were very large in size.
4) Production of the heat was in large amount in first generation computers.
5) Machine language was used for programming.
6) First generation computers were unreliable.
7) They were difficult to program and use.
Advantages:
-
Vacuum tubes were the only electronic components available during those days.
-
Vacuum tube technology made possible the advent of electronic digital computers.
-
These computers were the fastest calculating devices of their time. They could perform computations in milliseconds.
Disadvantages:
-
Too bulky in size.
-
Unreliable.
-
Thousands of vacuum tubes that were used emitted large amount of heat and burnt out frequently.
-
Air conditioning required.
-
Prone to frequent hardware failures.
-
Constant maintenance required.
-
No portable.
-
Manual assembly of individual components into functioning unit required.
-
Commercial production was difficult and costly.
-
Limited commercial use.
Examples:
UNIVAC, EDVAC, EDSAC and ENIAC computers are examples of first generation computing devices.