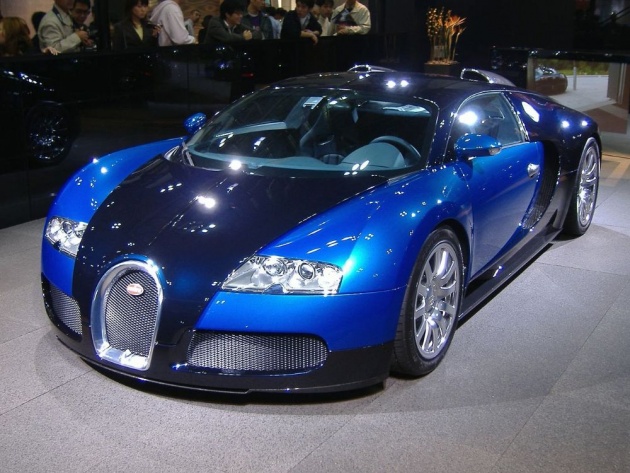
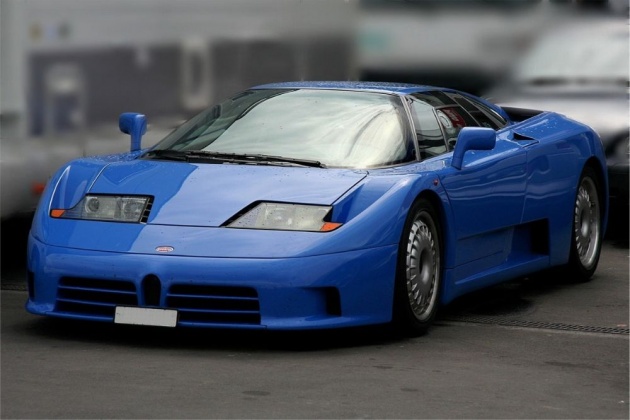
Automobiles Ettore Bugatti was a French car manufacturer of high-performance automobiles, founded in 1909 in the then German city of Molsheim, Alsace by Italian-born Ettore Bugatti. Bugatti cars were known for their design beauty (Ettore Bugatti was from a family of artists and considered himself to be both an artist and constructor) and for their many race victories. Famous Bugattis include the Type 35 Grand Prix cars, the Type 41 "Royale", the Type 57 "Atlantic" and the Type 55 sports car.
The death of Ettore Bugatti in 1947 proved to be the end for the marque, and the death of his son Jean Bugatti in 1939 ensured there was not a successor to lead the factory. No more than about 8,000 cars were made. The company struggled financially, and released one last model in the 1950s, before eventually being purchased for its airplane parts business in the 1960s. In the 1990s, an Italian entrepreneur revived it as a builder of limited production exclusive sports cars. Today, the name is owned by German automobile manufacturing group Volkswagen.
Under Ettore Bugatti
Founder Ettore Bugatti was born in Milan, Italy, and the automobile company that bears his name was founded in 1909 in Molsheim located in the Alsace region which was part of the German Empire from 1871 to 1919. The company was known both for the level of detail of its engineering in its automobiles, and for the artistic way in which the designs were executed, given the artistic nature of Ettore's family (his father, Carlo Bugatti (1856–1940), was an important Art Nouveaufurniture and jewelry designer).
World War I and its aftermath
During the war Ettore Bugatti was sent away, initially to Milan and later to Paris, but as soon as hostilities had been concluded he returned to his factory at Molsheim.[1] Less than four months after the Versailles Treaty formalised the transfer of Alsace from Germany to France, Bugatti was able to obtain, at the last minute, a stand at the 15th Paris motor show in October 1919.[1] He exhibited three light cars, all of them closely based on their pre-war equivalents, and each fitted with the same overhead camshaft 4-cylinder 1,368cc engine with four valves per cylinder.[1] Smallest of the three was a "Type 13" with a racing body (constructed by Bugatti themselves) and using a chassis with a 2,000 mm (78.7 in) wheelbase.[1] The others were a "Type 22" and a "Type 23" with wheelbases of 2,250 and 2,400 mm (88.6 and 94.5 in) respectively.[1]
Racing successes
The company also enjoyed great success in early Grand Prix motor racing: in 1929 a privately entered Bugatti won the first ever Monaco Grand Prix. Racing success culminated with driver Jean-Pierre Wimille winning the 24 hours of Le Mans twice (in 1937 with Robert Benoist and 1939 with Pierre Veyron).
Bugatti cars were extremely successful in racing. The little Bugatti Type 10 swept the top four positions at its first race. The 1924 Bugatti Type 35 is probably the most successful racing car of all time, with over 2,000 wins.[citation needed] The Type 35 was developed by Bugatti with master engineer and racing driver Jean Chassagne who also drove it in the car’s first ever Grand Prix in 1924 Lyon.[2] Bugattis swept to victory in the Targa Florio for five years straight from 1925 through 1929. Louis Chiron held the most podiums in Bugatti cars, and the modern marque revival Bugatti Automobiles S.A.S. named the 1999 Bugatti 18/3 Chiron concept car in his honour. But it was the final racing success at Le Mans that is most remembered—Jean-Pierre Wimille and Pierre Veyron won the 1939 race with just one car and meagre resources.
Aeroplane racing
In the 1930s, Ettore Bugatti got involved in the creation of a racer airplane, hoping to beat the Germans in the Deutsch de la Meurthe prize. This would be theBugatti 100P,[3][4] which never flew. It was designed by Belgian engineer Louis de Monge who had already applied Bugatti Brescia engines in his "Type 7.5" lifting body.
Railcar
Ettore Bugatti also designed a successful motorised railcar, the Autorail (Autorail Bugatti).[5]
Family tragedy
The death of Ettore Bugatti's son, Jean Bugatti, on 11 August 1939 marked a turning point in the company's fortunes. Jean died while testing a Type 57 tank-bodied race car near the Molsheim factory.