Practical
Apparatus Required
Galvanometer, HRB (high resistance box), LRB (low resistance box), Battery of voltage V, switch S etc.
Procedure
The galvanometer, Battery, HRB and switch are connected in series as shown in figure.
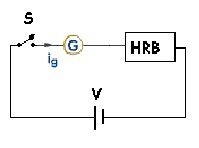
When the switch S is closed, the galvanometer shows deflection. Change the Resistance in HRB until the galvanometer shows maximum deflection. It means the deflection is made proportional to applied voltage V or maximum current at that instant.
The net voltage here is
V = Ig( Rg + R)
Here Rg and Ig are resistance of galvanometer and current through galvanometer, respectively. We find Rg and Ig by half scale deflection method.
Half scale deflection method
Full scale deflection is attained by changing resistance of HRB in circuit as shown above. Then LRB is connected in parallel with galvanometer without any other changes and disturbance in above circuit.
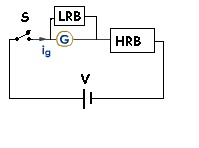
Changing resistance in LRB, galvanometer is set to half scale deflection. The current distributes itself into two equal parts, it means that resistance of LRB is equal to resistance of galvanometer.
Ig is calculated from above “eq” by putting the values of R, Rg and V.
For desired range ammeter, that much value of current for I is put in eq1 and Rs is calculated. That much resistance is connected in parallel with galvanometer to make it an ammeter of that desired range.
eq--------------1 (I - Ig) Rs = IgRg
Calculations (Ammeter measuring upto 3 Amps)
Example
Observations:
Full scale deflection
V=6V,
R=500Ω.
Half scale deflection
Rg=22Ω.
Putting in eq
V = Ig(Rg + R)
6 = Ig(22+500)
Ig = 6/522
Ig = 0.01A.
For desired range ammeter
Rg=22Ω,
Ig=0.01A,
We want to make an ammeter which measures up to 3 Amperes, then
I=3A.
Putting these values in eq1
(I - Ig)Rs= IgRg
Rs= IgRg/(I-Ig)
Rs= (0.01)(22)/(3-0.01)
Rs= 0.22/2.99
Rs=0.07335Ω
Rs= 73.3m Ω
This is the required resistance which is to be connected in parallel to galvanometer to convert it into 3 A ammeter.



