Earlier, I wrote the theory about the working of galvanometer as voltmeter. Today I am going to write the procedure of making voltmeter from galvanometer practically in a lab.
Practical
Apparatus Required:
Galvanometer, HRB (high resistance box), LRB (low resistance box), battery of voltage V, switch S etc.
Procedure:
The galvanometer, battery, HRB and switch are connected in series as shown in figure,
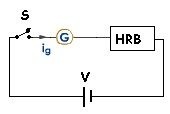
When the switch S is closed, the galvanometer shows deflection. Change the resistance of HRB until the galvanometer shows maximum deflection. It means that the deflection is made proportional to applied voltage V.
The net Voltage is then
V= Ig(R+Rg) ----------1
R= (V/Ig) - Rg ----------2
Ig is the current in the circuit, Rg is the resistance of the Galvanometer and R is the resistance of the HRB.
To convert galvanometer in to desired range voltmeter that much value of voltage is put in second equation. Rg and Ig are known, R can be calculated which is then connected in series with galvanometer to get a desired range voltmeter.
Ig and Rg can easily be found by half scale deflection method.
Half scale deflection:
Full scale deflection is attained by changing the resistance of the HRB in above shown circuit. Then LRB is connected in parallel with galvanometer without any other changes or disturbance in the above circuit.
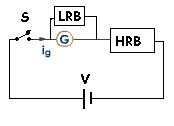
Changing resistance in LRB, galvanometer is set to half scale deflection. The current distributes itself into two equal parts, it means resistance of the LRB at that instant is same as the resistance of the galvanometer. So Rg is calculated by looking onto the resistance of LRB in half scale deflection. Ig is calculated with the help of 1st equation by putting values of R, Rg and V.
For desired range voltmeter, that much value of voltage V is put in eq-2 and R is calculated. That R is connected in series with galvanometer to get a desired range voltmeter.
Precautions:
HRB should not be disturbed after full scale deflection. Keys must be put properly in the boxes.



