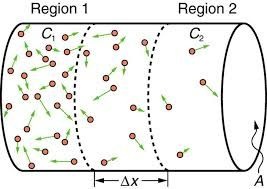
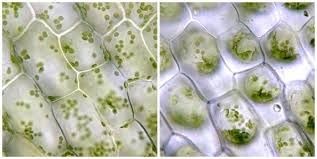
Diffusion:
The movement of molecules (may be solid liquid or gas) of a substance from the region of higher concentration (Where the particles are more ) to region of lower concentration(where the particles are less) is called diffusion. No energy is required for diffusion. Hence diffusion is type of passive transport. Photosynthesis and respiration in the plant cells take place by diffusion. Water, oxygen, carbon dioxide and some other molecule can diffuse across the cell membrane by the process of diffusion. Diffusion is a slow process but it fulfills all the gaseous requirements of the plants. Gas exchange in gills of fish and lungs of mammals occur through diffusion. The efficiency of diffusion depends on.
I. Distance covered
ii. Concentration gradient or difference in concentration.
iii. The kinds of molecules i.e. solid, liquid and gas.
For example if we spray perfume in one corner of the room, its fragrance will gradually spread by diffusion in all parts of the room. The speed of diffusion depends on the type of material i.e. solid liquid or gas.
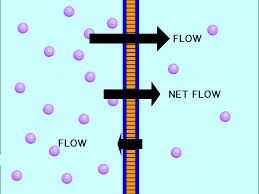
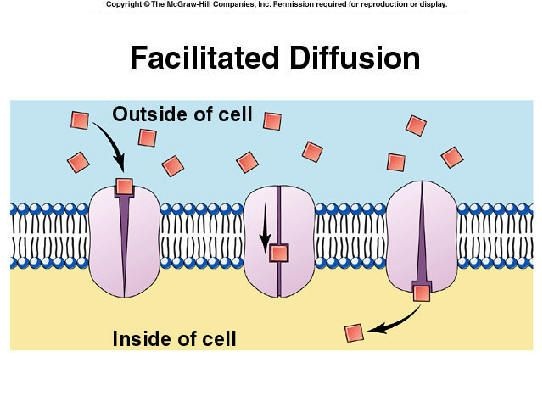
Facilitated diffusion:
Some molecule does not pass freely across the cell membrane because of their size or charge. Such molecules diffuse out of the cell with the help of transport protein present in cell membranes. It is called facilitated diffusion. The rate of facilitated diffusion is higher than simple diffusion. It is type of passive transport because there is no expenditure of energy in this process.
Osmosis:
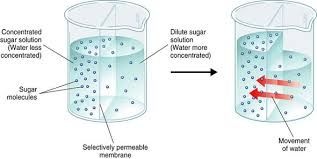
The movement of solvent molecule like water from its higher concentration to lower concentration area through semi permeable membrane is called osmosis. It is type of diffusion in which selective substance can pass through a membrane while other substances cannot. Such membrane which allows selective materials to pass into or out of the cell is called semi permeable membrane or selectively permeable membrane. This special kind of diffusion that occurs through a semi permeable membrane is called osmosis.
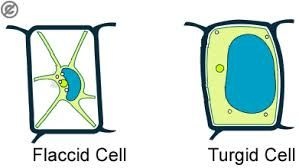
Turgid cell and turgor in plant cells:
When a plant cell is surrounded by sufficient water then water moves into the vacuole of the cell by osmosis. Due to strong cell wall, plant cell does not rupture but the cell become hard ad tough. This condition is called turgidity and the cell is said to be turgid. The internal pressure exerted on the cell wall is called turgor pressure. Turgidity makes the stem and leaves to be tough and hard. Turgor maintains the shape of the plant. The closing and opening of stomata occurs due to the change in turgor. Some flower open at day time and some flower open at night time. Upward movement of water and dissolved salts in plants occur due to turgor.
Plasmolysis:
The process in which water comes out from the cell and protoplasm of the cell become shrink and pulled away from the cell wall is called plasmolysis. Such a cell is said to be plasomlysed.
Deplasmolysis:
When plasmolysed cell is placed in a water or solution of higher water concentration then water enters into the cell by osmosis. The cell become turgid and csuch a cell is called deplamolysed and the process is called deplasmolysis.
Effect of different solution on plant cell and animal cell:
When animal cell is placed in hypotonic solution (hypotonic solution are those that have less solute may be pure water), water enters into the cell by osmosis. Animal cell swells like balloon and become lysed or burst. But the plant cell become turgid in hypotonec solution and do not burst due to strong cell wall.
When both animal and plant cells are placed in isotonec solution(isotonic solution have equal solute to that of inside a cell) both cell remain normal.
When both plant and animal cells are placed in hypertonic(hypertonic solutions have more solute than inside of a cell) water comes out of the cell by osmosis. The shrinkage of protoplasm occurs in both the cells.