Introduction
My first blog is about one of the greatest international humanitarian organization known as Doctors Without Borders (Médicins Sans Frontières) - MSF - which offers medical aid to people affected by severe humanitarian crisis. Another MSF's mission is to tall attention to the difficulties faced by the patients that receive medical care in their projects around the world.

Photo credit: Global Research
The organization was established in 1971, in France, by young doctors and journalists, who worked as volunteers in the late 60s in Biafra, Nigeria. While helping victims in a huge and cruel civil war, the professionals realized the limitations that an international humanitarian aid suffers: the difficulty to access the place in need of help and all the bureaucratic and political barriers that silenced many, even before terrible situations. With that said, Doctors Without Borders arises as a humanitarian organization that associates medical aid and public awareness about the suffering of their patients, giving visibility to realities that cannot remain neglected. In 1999, MSF received the Nobel Peace Prize.
The Activities
Above all, the work of Doctors Without Borders is providing medical assistance. The organization offers health aid and preventive care to those in need, regardless the country in which people are located.
In situations where the medical performance is not enough to ensure the survival of certain population – as it occurs in cases of extreme urgency –, the organization can provide water, food, sanitation and shelter. This type of action happens mainly in times of crisis, when the previous balance of a situation is broken and people’s lives are threatened.
The work of MSF respects the rules of medical ethics, in particular, the duty to offer aid without harming any individual or group and the impartiality, ensuring the right to confidentiality. No one can be punished for exercising a medical activity in accordance with the professional code of ethics, regardless of the circumstances or the beneficiaries may be.
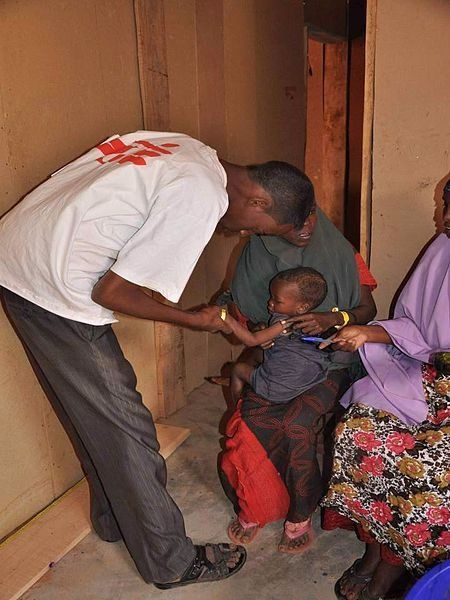 Photo credit: Wikimedia Commons
Photo credit: Wikimedia Commons
Principles of the Organization
Doctors Without Borders offers humanitarian and medical help to people in danger and to victims of natural and man-made disasters and conflict situations, without any racial, religious, philosophical and political discrimination.
Based on its neutral and impartial work, Doctors Without Borders claims, in the name of the universal medical ethics and humanitarian assistance rights, total and complete freedom of the activities it performs. The members of the organization strive to respect the deontological of their profession and to maintain complete independence in relation to all power, as well as to any political, economic and religious force. Working as volunteers, they understand the risks and dangers of the work they perform and do not claim for themselves any compensation other than the one offered by the organization.
Engagement of the Organization
Emergency situations must have quick responses, with specialized medical care and logistical support, but chronic failures in the local health system, is that to say, the lack of health facilities, skilled professionals and the absence of the offer of free services to populations without financial resources, can also motivate the actions of the organization.
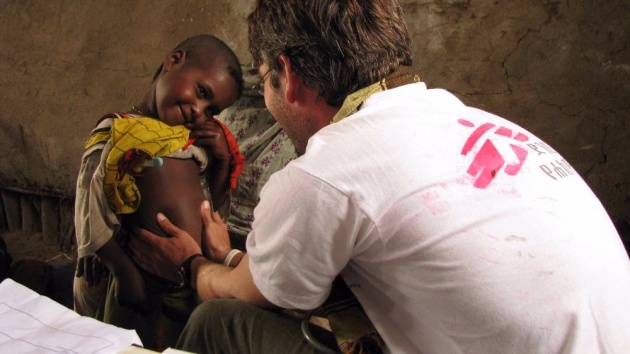
Photo credit: The Borgen Project
Acting in an independent, neutral and impartial way, MSF determines to its own evaluation, where, when and how to act. When acting in response to a sudden emergency such as a neutral disaster, it can be made possible between 48 and 72 hours. Behind MSF’s agility hides an extremely efficient logistics system: in 1980, the organization began using customized and adapted kits to each context, which are prepackaged and ready to go and are constantly improved. The kits contain medicines, supplies and basic equipment and are used nor only in vaccination campaigns but also in the installation of an inflatable hospital.
MSF also tries to join patient groups to sensitize and, sometimes, to pressure the actors involved – international bodies and institutions and the pharmaceutical industry – so that the populations extremely in need have the access to quality medicines.



