Ebola Outbreak
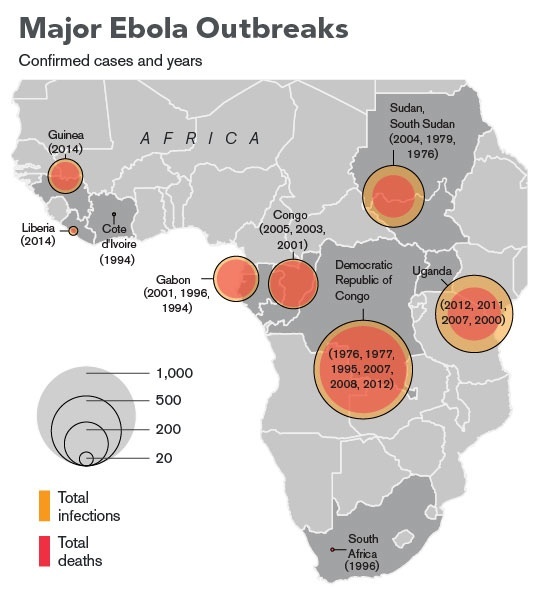
The image above shows the history of Ebola outbreaks in Africa. Notice the dates in the top left corner of the image for Guinea and Liberia - 2014. Unfortunately, the outbreak has spread into Sierra Leone since the map was posted in April earlier this year. Ebola is a deadly and infectious virus that causes internal and external bleeding in its victims, killing nearly 90% of those who are infected. Previous ebola outbreaks were thousands of miles away, impacting areas of Sudan and the Democratic Republic of Congo - as seen in the above image.
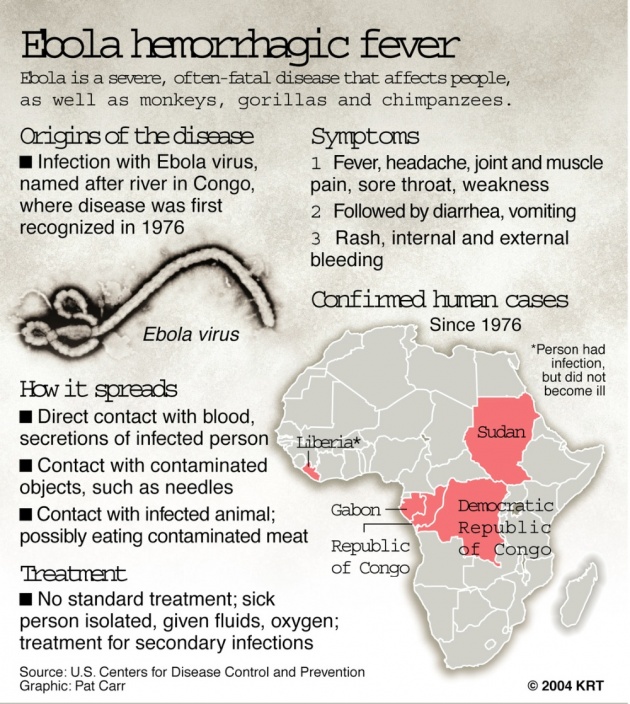
The Ebola virus is spread by close contact with other and is highly contagious. There are also no known vaccines or treatment for those who are infected. It takes approximately 2 to 21 days for the virus to fully infect its victim. The beginning stages and symptoms of Ebola are common symptoms with any virus, headaches, sore throats, weakness, etc. However, as the virus continues to spread throughout the body, the symptoms become much more severe, leading to raised rashes and bleeding - both internal and external.
The Ebola outbreak began earlier this year in Guinea, quickly spreading into surrounding countries of Liberia and Sierra Leone. Surrounding countries took precautions and suspended traveling to particular areas, with travel being one of the easiest ways to spread Ebola. However, these African countries have thousands of refugees that travel between countries effortlessly, making it difficult to quarantine the infected individuals and communities.
Results of the Ebola Outbreak
On July 6, the Guinea Ministry of Health released reports that over 400 suspected cases of the Ebola virus have been reported, with 307 of those cases resulting in fatalities. 294 of those cases have been confirmed by laboratory testing in Guinea. Sierra Leone also released reports on July 6, stating over 300 suspected cases with 269 of those cases being confirmed by laboratory testing - 127 of those cases resulting in fatalities. Following the Guinea and Sierra Leone reports, Liberia released reports of over 130 suspected cases of the Ebola virus, with 63 cases being confirmed by laboratory testing - 84 of those cases resulting in fatalities.

The Ebola outbreak has lead to a combined total of 830 suspected cases, with 626 of those cases being confirmed. Of the 830 suspected cases of the Ebola virus, 518 of those cases have already lead to fatalities. After analyzing the virus, it has been reported that it is 94% similar to the virus in previous outbreaks in the Democratic Republic of Congo. The CDC (Centers for Disease Control) is in full communication with partners in these areas, and is assisting in the battle to quarantine and isolate the virus.
Guinea, Sierra Leone and Liberia have also teamed up to help fight the Ebola outbreak. The Ministry of Health and Sanitation of Sierra Leone, the Ministry of Health and Social Welfare of Liberia and the Guinean Ministry of Health are working with partners to respond and further investigate the current Ebola outbreak. A great way to help fight the current and severe Ebola outbreak is to teach others and spread awareness. Education and awareness are crucial steps in fighting any disease.
#AfricaNews
Thank you for participating in the very first #AfricaNews post on Greater-Tomorrow! We will be posting updated news about current events in Africa and using the hashtag #AfricaNews so other users can follow, comment and participate in our conversations and updates. Please subscribe to Greater-Tomorrow on Film Annex at http://www.FilmAnnex.com/Greater-Tomorrow. Follow us on Twitter @Greater_T and like us on Facebook at http://www.Facebook.com/GreaterT!



