The recently disclosed FREAK (Factoring attack on RSA Export Keys) attack is an SSL/TLS vulnerability that is affecting major browsers, servers and even mobile devices.
FREAK vulnerability allows the attacker to intercept HTTPS connections between vulnerable clients and servers and force them to use weakened encryption, which the attacker can break to manipulate or steal sensitive data.
Although most major hardware/software vendors and owners have patched this flaw, many are still susceptible to this kind of attack.
Instrumental in discovering FREAK flaw, the University of Michigan conducted scans and discovered that an estimated 36.7% of the 14 million websites offering browser-trusted certificates were vulnerable at the time of disclosure.
This includes some very high profile pages like nsa.gov, irs.gov and even the ubiquitous connect.facebook.com (the source of all Facebook "Like" buttons.)
IMPACTS OF FREAK ATTACK
Intercepts your sensitive, encrypted, web sessions via a man-in-the-middle attack, putting your clients at risk
Redirects users to malicious sites and harvests credentials, giving attackers the ability to pivot and attack your environments directly and steal sensitive data (intellectual property)
Forces weak encryption, even if you use a strong encryption method, making stealing your data much easier
Affects a large number of vendors including every Windows version, Apple’s mobile and desktop operating systems, and Google Android
HOW TO PROTECT AGAINST FREAK?
AlienVault Unified Security Management (USM) can help. USM provides asset discovery, vulnerability assessment, threat detection (IDS), behavioral monitoring and SIEM in a single console.
USM can scan your network to identify assets with the FREAK vulnerability, making it easy for you to identify systems that need to be patched and prioritize remediation.
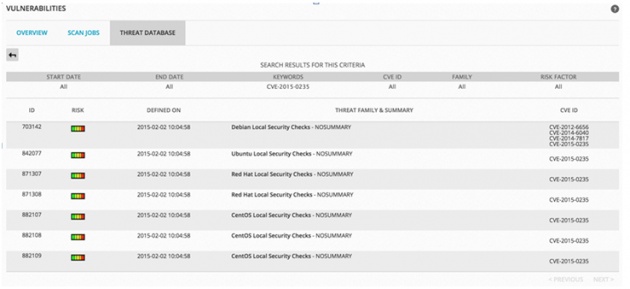
Not only can USM identify vulnerable systems, it can also help you detect attempted exploits of the vulnerability. Within hours of the discovery of the FREAK vulnerability, the AlienVault Labs team pushed updated correlation directives to the USM platform, enabling users to detect attackers attempting to exploit it.
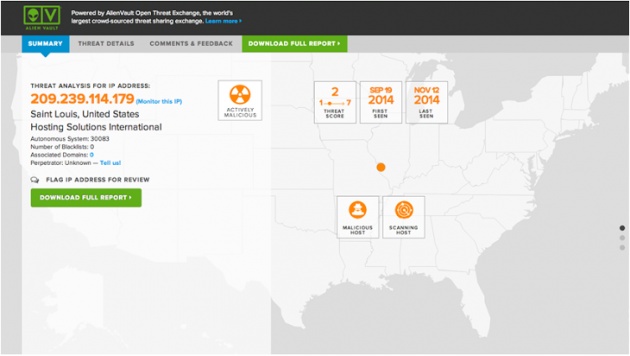
USM also checks the IP information against the Open Threat Exchange (OTX), the largest crowd-sourced threat intelligence exchange. In the example below, you can see details from OTX on the reputation of an IP, including any malicious activities associated with it.