Sedimentology is closely related to Stratigraphy. Sedimentology is related to the study of sediments such as sand, silt, clay and mud, and the processes which result in their deposition. Geologists apply the knowledge of sedimentology to explain the geological history through the observations of sedimentary rocks and sedimentary structures.
Stratum (Plural: Strata): A bed of sedimentary rock or sedimentary deposit having approximately the same composition and physical properties throughout.
i) Geochemistry: It deals with the study of chemistry: i.e. chemical properties and constituents of the minerals, rocks, deposits, strata, etc.
ii) Geophysics: It deals with the study of the principles, processes, phenomena and methods of physics e.g. mechanical waves and vibrations, heat and thermodynamics, electricity & magnetism, sound & acoustics (used in SONAR), light & optics, radiations and radio-activity, radio-waves (used in RADAR) and x-rays, other electromagnetic and LASER radiations etc. applied to explore certain sub-surface economic minerals, oil & gas, water sources or certain geological features or to obtain certain sub-surface information or examine certain sub-surface geological features or ground (to be used as foundation) or to solve certain geological problemsiii) Geohydrology or Hydrogeology: It emerged due to the interaction of geology and hydrology. Geohydrology or Hydrogeology deals with the study of geological aspects of ground water and deep sub-surface water in regard to their occurrence and movement through the different strata and rocks.
iv) Mining Geology: It deals with the study of geological knowledge used in Mining (Underground Mining as well as Surface Mining) and Quarrying, for the exploration, development and exploitation of the economic mineral deposits.
v) CIVIL ENGINEERING GEOLOGY OR ENGINEERING GEOLOGY: It emerged due to the interaction of geology and civil engineering works. Engineering Geology deals with the application of geological knowledge applied to the Civil Engineering Projects for the safe, stable and economic designing and construction. Good knowledge of Engineering Geology is very essential for the study of Building Materials / Civil Engineering Materials, Soil Mechanics, Earthwork, Geotechnical Engineering, Foundations’ Engineering (for the foundations of huge structures), Strength of Materials and for the designing and construction of Highway, Motorway, Railway, Runway, Bridge, Tunnel, Dam and Reservoir.
Engineering Geology plays a vital role in the planning, designing and construction of safe, stable and economic construction.
vi) Rock Mechanics: It deals with the study of behaviour of the rocks subjected to various loading conditions. Rock Mechanics is more engineering oriented than an applied subject or an ordinary science subject. But as the rocks are the geological bodies and behaviour of the rocks is practically controlled by the nature, properties and constitution of the rocks; therefore this subject includes full geological knowledge of the rocks. In Rock Mechanics, the applied load may be natural or artificial, static or dynamic. Similarly, the tests and measurements carried out while studying Rock Mechanics may be made in laboratory or in-situ environment or combination of both.
vii) Geo-mechanics: It deals with the study of the natural field of forces acting on regional and global level. Geo-mechanical studies include the forces acting on continents, oceans, mountain-ranges, basins, valleys, plains, etc. In some books, Soil Mechanics and Rock Mechanics are included / shown as the sub-divisions or subjects of Geo-mechanics.
viii) Meteorology: It deals with the study of atmosphere which is an integral part of the earth, in all the aspects, physical, chemical and biological. About 50, 60 years ago it was thought that Meteorology was concerned with the weather only.
With the advancement in the space and upper atmosphere research and development, the effects of atmosphere upon rockets, space-ships, satellites, etc became very important and hence Meteorology became the science of immense significance.
ix) Oceanography: It deals with the study of all aspects of oceans. It is the youngest of all the geological sciences. Oceans play an important role as far as geological, industrial and military significance is concerne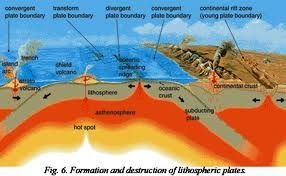
MPORTANCE OF ENGINEERING GEOLOGY: Engineering Geology deals with the application of geological knowledge to the Civil Engineering Projects for the safe, stable and economic designing and construction. Fundamentals of Engineering Geology is very essential to have a competent Civil Engineering expertise. The knowledge and application of Engineering Geology to the effective planning, designing and construction of a Civil Engineering Project is considered not only desirable but also essential.
UNDERSTANDING OF ENGINEERING GEOLOGY:
A Civil Engineer is neither expected nor required to undertake any geological study or investigation of the area for planning and designing purpose of a Civil Engineering work. However, he must be capable of understanding a geological condition, information and problem of an area and certainly capable of understanding of and critically discussing a geological problem or report with an expert geologist and obtain, rather implement the maximum useful geological information to that task or problem.
THE UNIVERSE
Stellar System – Galaxy – Solar System: Mercury, Venus, The EARTH, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto.
Three Important Parts i.e. Three Spheres of The Earth:
Atmosphere:
Gaseous part
Extends from the earth-surface to 700 km or even beyond
Makes one-millionth part of the total mas of the earth
Held by Gravitational Pull of the earth
Constitutes the mixtures of following gases (by volume): Nitrogen = 78.084% Oxygen = 20.946%
Argon = 0.934% Carbon Dioxide = 0.033%
All the other gases = 0.003%
Three Important Parts i.e. Spheres of The Earth:
This composition remains uniform up to 80 to 100 km.
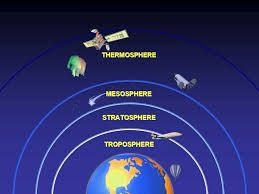
Atmosphere is further sub-divided into:
(i) Troposphere – lowermost zone – extends up to about 9 and 18 km.
There is a drop in temperature of about 6 OC/km upward
(ii) Stratosphere – extends from 9 and 18 km to 40 km
Mainly comprises ozone layer - acts as natural shield against the ultraviolet rays of the sun
(iii) Mesosphere – extends from 40 to 80 km
At –100 OC
(iv) Thermosphere – extends from 80 to 100 km
(v) Ionosphere – extends beyond 100 km
Entirely composed of electrically charged ions
Three Important Spheres of The Earth:
(ii) Lithosphere:
Stony part of the earth
Composed of solid materials
Extending from the earth surface down to the centre of the earth
Comprises: The Crust, The Mantle and The Core
Hydrosphere:
Comprises all the bodies of water occurring on or below the surface of the earth
Makes only 0.03% of the total mass of the earth
Constitutes about 75% of the earth surface by volume
More than 98% of the hydrosphere is made up of saline waters called oceans and seas
First Component of the hydrosphere: Oceans and Seas
Second Component of the hydrosphere: Lakes, Ponds, Springs, Streams, Canals and Rivers
Third Component of the hydrosphere: Huge bodies of frozen water in form of Snow and Glaciers
Fourth Component of hydrosphere: water occurring in the pores, cavities, pockets and cracks of the soil and rocks in the earth crust - called Ground-water



