Guava Nutrition Facts
Guava is another tropical fruit rich in high-profile nutrients. With its unique flavor, taste, and health-promoting qualities, the fruit easily fits in the new functional foods category, often called “super-fruits.”
It is an evergreen, tropical shrub or low-growing small tree probably originated in the central Americas. Guavas actually thrive in both humid and dry climates and can tolerate brief periods of cold spells, but can survive only a few degrees of frost. Adaptability makes it a favorite commercial crop in some tropical areas.
Botanically, this wonderful fruit belongs within the family of Myrtaceae, in the genus: Psidium. Scientific name:Psidium guajava.
 |
 |
| Ripe guava fruits on Psidium guajavatree. | Red varieties are indeed rich in carotenes and lycopene. |
During each season, the guava tree bears numerous round, ovoid or pear-shaped fruits that are about 5-10 cm long and weigh around 50–200 g. Different cultivar types of guava grown all over the world which, vary widely in flavor, pulp color, and seeds.
The fruit is soft when ripe with sweet musky aroma and creamy in texture. Internally, its flesh varies in color depending up on the cultivar and may be white, pink, yellow, or red. Ripe fruits have rich flavor with sweet-tart taste. Each fruit contains numerous tiny, semi-hard edible seeds, concentrated especially at its center.
Health benefits of guava fruit
-
Guava is low in calories and fats but contain several vital vitamins, minerals, and antioxidant poly-phenolic and flavonoid compounds that play a pivotal role in prevention of cancers, anti-aging, etc.
-
The fruit is very rich source of soluble dietary fiber (5.4 g per 100 g of fruit, about 14% of DRA), which makes it a good bulk laxative. The fiber content helps protect the colon mucous membrane by decreasing exposure time to toxins as well as binding to cancer-causing chemicals in the colon.
-
Guava-fruit is an excellent source of antioxidant vitamin-C. 100 g fresh fruit provides 228 mg of this vitamin, more than three times the DRI (daily-recommended intake). The flesh just underneath its outer thick rind contains exceptionally higher levels of vitamin C than its inner creamy pulp.
-
Scientific studies shown that regular consumption of fruits rich in vitamin C helps human body develop resistance against infectious agents and scavenge cancer causing harmful free radicals from the body. Further, it is required for collagen synthesis within the body. Collagen is the main structural protein in the human body required for maintaining integrity of blood vessels, skin, organs, and bones.
-
The fruit is a very good source of Vitamin-A, and flavonoids like beta-carotene, lycopene, lutein and cryptoxanthin. The compounds are known to have antioxidant properties and therefore essential for optimum health. Further, vitamin-A is also required for maintaining healthy mucus membranes and skin. Consumption of natural fruits rich in carotene is known to protect from lung and oral cavity cancers.
- 100 g of pink guava fruit provides 5204 µg of lycopene, nearly twice the amount than in tomatoes. (100 g tomato contains 2573 µg of lycopene). Studies suggest that lycopene in pink guavas prevents skin damage from UV rays and offers protection from prostate cancer.
-
Fresh fruit is a very rich source of potassium. It contains more potassium than other fruits like banana weight per weight. Potassium is an important component of cell and body fluids that helps controlling heart rate and blood pressure.
-
Further, the fruit is also a moderate source of B-complex vitamins such as pantothenic acid, niacin, vitamin-B6 (pyridoxine), vitamin E and K, as well as minerals like magnesium, copper, and manganese. Manganese is used by the body as a co-factor for the antioxidant enzyme, superoxide dismutase. Copper is required for the production of red blood cells.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percentage of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 68 Kcal | 3.5% |
| Carbohydrates | 14.3 g | 11.5% |
| Protein | 2.55 g | 5% |
| Total Fat | 0.95 g | 3% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 5.4 g | 14% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 49 µg | 12.5% |
| Niacin | 1.084 mg | 7% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.451 mg | 9% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.110 mg | 8.5% |
| Riboflavin | 0.040 mg | 3% |
| Thiamin | 0.067 mg | 5.5% |
| Vitamin A | 624 IU | 21% |
| Vitamin C | 228 mg | 396% |
| Vitamin E | 0.73 mg | 5% |
| Vitamin K | 2.6 µg | 2% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 2 mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 417 mg | 9% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 18 mg | 2% |
| Copper | 0.230 mg | 2.5% |
| Iron | 0.26 mg | 3% |
| Magnesium | 22 mg | 5.5% |
| Manganese | 0.150 mg | 6.5% |
| Phosphorus | 11 mg | 2% |
| Selenium | 0.6 mcg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.23 mg | 2% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-β | 374 µg | -- |
| Crypto-xanthin-β | 0 µg | -- |
| Lycopene | 5204 µg | -- |
Selection and storage
In the tropical region, guavas can be readily available year around. Red flesh variety such as "Thai maroon" flesh guavas are rich in nutrition than green-apple guavas. Oftentimes, the fruits are left to ripen on the tree to experience their intense, natural flavor. They can also be picked while green but mature, and later allowed to ripen at room temperature. Ripe guavas have a characteristic color and pleasant aroma.
In the stores, buy fresh fruits featuring intact skin without any cuts, bruises, or patches. Placing the fruit wrapped in a paper with a banana or apple will hasten their ripening process.
Mature, yet green fruits may be stored for two to five weeks under ideal, regulated temperature between 46°F and 55°F, and relative humidity of 85 to 95 percent. Over-ripe fruits may keep well inside the refrigerator only for few days.
Preparation and serving methods
Wash them in cold running water in order to remove any dust or insecticide residues. Fresh ripe guava is best enjoyed with its skin. Remove any floral remnants (sepals) at the apex, and then trim either ends with a sharp knife. It can be cubed, or sliced into, as in apples.
Here are some serving tips:
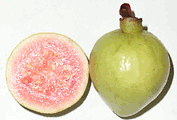 |
| Guava fruits, pink-flesh variety. |
-
Eat fresh guava as it is, to enjoy its natural flavor and unique taste.
-
Guava fruit juice is a popular delicious drink in many parts.
-
Sliced guava-cubes are a great addition to fruit salads.
-
It is also often used in dessert preparations.
-
The fruit is also extensively used to make candies, preserves, jellies, jams, marmalade, etc.
-



