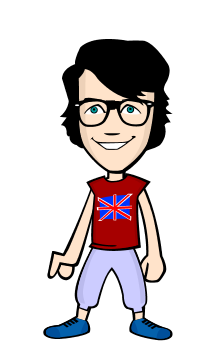
First of all Greek philosophers thought that matter is made up of indivisible particles which cannot be further sub-devided. Democritus (460---370 B.C) called these indivisible particles as atoms. (Greek word atoms means indivisible). In 1808, an English school teacher John Dalton Gave atomic theory. Its main points are given below.
1.All matter is composed of atoms.
2.The atoms of same elements have similar properties.
3.The atoms of different elements have different properties.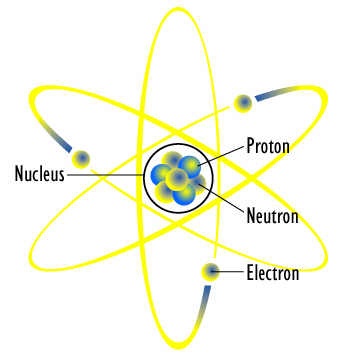
The modern definition of atom is given below.
The smallest particle of an element which may or may not exist independently is called atom. e.g He, Ne, H, C, Na, Cu, S, etc. Modern research shows that an atom is further composed of electrons, protons, neutrons, positrons, hyprones, neutrino and anti-nutrino etc. They are called sub-atomic particles. More than 100 sub-atomic particles have been discovered. But electron, proton and neutron are the fundamental particles of an atom. In (1779---1848) Berzelius a Swedish chemist determined the atomic masses of elements. Moreover he introduced symbols for elements.
The evidence of atom is given below. A clear image of an atom cannot be obtained because it is smaller than wave length of visible light. An ordinary microscope can measure Upto or above 500 nm. An atom can be observed in an electron microscope. An electron microscope uses beam of electrons instead of visible light. The X---ray work also gives evidence of atoms. The diameter of the atoms is of the order of 2×〖10〗^(-10) m or 0.2 nm (1 nm=〖10〗^(-9 )m). The mass of an atom ranges from 〖10〗^(-27) kg to 〖10〗^(-25) kg. We may say that an atom is extremely small particle. A student can imagine that a full-stop can contains two millions atoms in it. A Photograph of graphite obtained by electron microscope is shown in the figure. This photograph has been magnified 15 millions times.