1
Increase your caloric consumption. For example, if you are currently consuming 2,000 calories a day, boost that to about 2,500 calories or even more. But make sure that you're eating clean, and are not eating too much.

2
Get enough protein to support muscle growth. Aim for between 1-1.8 grams of protein per kilogram of bodyweight. For example, if you weigh 180lb, take in at least 81-146g—or about 2.8-5oz—of protein every day.

3
Drink enough water. The body needs a sufficient amount of water to build muscle at an optimal rate. Here's a great little formula to help make sure you are getting enough: Bodyweight in lbs X 0.6 = water intake in ounces.
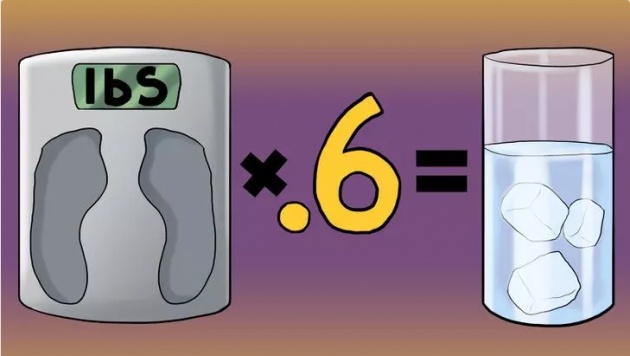
4
Eat regularly. Rather than having two or three large meals during the day—something we've grown up with—change your eating habits so that you are eating five or six smaller meals during the day.
To help keep your protein intake high, one or two of those meals can be a protein shake. Here's one example, though a quick Internet search will uncover hundreds of delicious protein shakes:
8oz skimmed milk
1 banana
1 tbsp peanut butter
2 scoops of protein powder

5
Eat healthy fats. That's right—not only does it make food taste good, fat is good for you, as long as you are eating the right kinds and amounts of fat! Saturated fats—the fat you'll find in a stick of butter, a bag of chips, or bacon—should be limited to about 20g or less. That's the bad news. The good news is that unsaturated fats are actually beneficial, even necessary. Fat is necessary for the proper distribution of vitamins A, D, E, and K, helps promote better eyesight, and healthy skin. Depending on your total caloric intake, 50-70g of monounsaturated or polyunsaturated fat is beneficial for your training, and your overall general health.
Monounsaturated fats can be found in olive, canola, and sesame oils; avocado; and nuts such as almonds, cashews, peanuts, and pistachios.
Polyunsaturated fats are found in corn, cottonseed, and safflower oils; sunflower seeds and oils; flaxseed and flaxseed oil; soybeans and soybean oil.
Omega-3 fats, an overall winner of a fat that is very beneficial to heart and blood health, eyesight, and for children, brain development. You'll find this fat in many omega-3-enriched foods. Another great source is fatty cold-water fish such as salmon, tuna, trout, and sardines.
A good way to determine how much fat in grams you should be taking in is to multiply your calorie intake by 0.001 for maximum trans-fats; by 0.008 for maximum saturated fats; and by 0.03 for the "good fats". For example, for a 2,500-calorie diet, you would limit trans-fats to 3g or less, saturated fats to 20g or less, and up to 75g of mono- and polyunsaturated fats.