HSRP messages
There are 3 types of messages used:
- Hello: send to 224.0.0.2 by every router to indicate its status, such as Group ID, HSRP timer values, version, and authentication.
- Coup: send when a router wants to preempt or would like to become the active gateway
- Resign: send by the current active gateway when it resigns its role. Could be due to a shutdown or hearing better Hello or Coup preemption.
HSRP states
There are 6 stages a router passes in HSRP,
1) Disabled: router not participating in HSRP
2) Init: router not participating in HSRP
3) Listen: monitor Hello message from active gateway; standby gateways or other gateways ready for new election once active gateway fails.
4) Speak: backup gateway become standby gateway (enter Standby stage) and exchange messages with active gateway, which now enters Active stage.
HSRP authentication
HSRP ignores unauthenticated HSRP message and by default, Cisco devices use a plaintext authentication of ‘cisco’. You can change the password to another plain-text password with ‘(config-if)#standby GROUP_NO authentication text PASS’
You can configure MD5 passwords with ‘(config-if)#standby GROUP_NO authentication md5 key-string [0 | 7] PASS [timeout SEC]’, where password should be at least 16 characters (recommended) but less than 64 characters.
You can also use a key-chain instead with ‘(config-if)#standby GROUP_NO authentication md5 key-chain NAME’ where the key chain has to be previously configured.
If ‘0’ is used, this is equivalent to ‘standby authentication’ command, if ‘7’ is used, this password will be encrypted if ‘service password-encryption’ is enabled. As for the key chain configuration, you can use ‘key-string [0 | 7]’ when specifying it.
When this command is set, clear-text password become 0 indicating it’s disabled.
Timeout value is the time when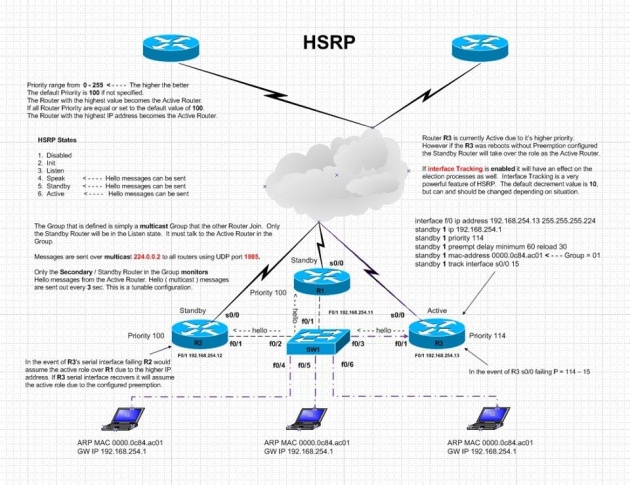 the password will become invalid.
the password will become invalid.



