HUMAN BODY PARTS
(Part 3)
In the previous lecture we have study that human brain is have neurons which are the cells that generate action potentials and convey information to other cells; these constitute the essential class of brain cells.
In addition to neurons, the brain contains Glial cells in a roughly 10:1 proportion to neurons. Human brain weighs about 1-1.5 kg. in today’s lecture we will study about Anatomy of Brain.
HUMAN BRAIN’S ANATOMY
We have previously study that Human Brains are extremely complex. For example, the human brain contains more than 100 billion neurons, each linked to as many as 10,000 others. The adult human brain is a 1.3 kg mass of pinkish-gray jellylike tissue made up of approximately 100 billion nerve cells, or neurons; neuroglia (supporting-tissue) cells; and vascular (blood-carrying) and other tissues.
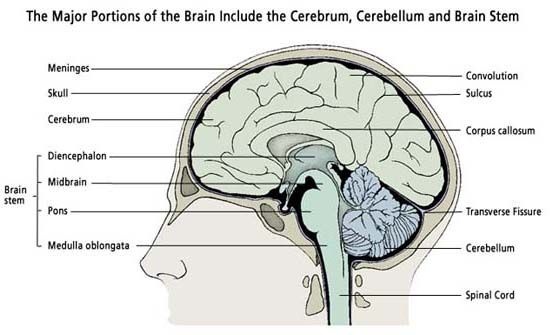
Neurons of human Brain transmit and analyze all communication within the brain and other parts of the support to the neurons. Three protective meanings (membranes) cover the brain. A clear liquid, the cerebrospinal fluid, surrounds the human brain and protects the internal portion from varying pressures. This fluid also transports chemical substances within the nervous system.
Brain is very complicated and it appears as three connected parts; the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brain stem. Two other major parts also exists which are thalamus and the hypothalamus. These parts of brain lie above the brain stem underneath the cerebellum. Most high-level brain functions take place in the cerebrum. Its two large hemispheres are divided into five lobes: the frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital lobes and the insula. The cerebrum receives information from the sense organs and sends motor commands (signals that stimulate activity in the muscles or glands to other parts of the brain and the body. Many areas of the cerebral cortex correspond to specific functions, such as vision, hearing, speech, emotions, thinking and remembering.
Cerebellum is the part which coordinates with body movements. It is divided into two lobes connected by a bundle of white fibers. The cerebellum coordinates voluntary movements by fine-tuning motor commands from the cerebrum. The cerebellum also maintains posture and balance by controlling muscle tone and sensing limb positions.
The brain stem is very important part and it is responsible for sustaining the basic functions of life, such as breathing and blood pressure. Sensory and motor nerve fibers connecting the brain with the rest of the body cross over to the opposite side in the brain stem. The left half of the brain communicates with the right half of the body and the right half of the brain with the left half of the body.
Twelve pairs of cranial nerves connect the brain with the head and neck. Some are motor nerves, controlling muscle movement. Some are sensory nerves, conveying information from the sense organs. Others contain fibber for both sensory and motor impulses.
That was about the Brain Anatomy. In the next lecture we will discuss other parts of the body.