LED Diode
 911electronic.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/Orange_LED_emitting-1024x682.png 1024w, 911electronic.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/Orange_LED_emitting.png 1148w" alt="led diode" width="300" height="200" />
911electronic.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/Orange_LED_emitting-1024x682.png 1024w, 911electronic.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/Orange_LED_emitting.png 1148w" alt="led diode" width="300" height="200" />
Light-emitting diode (LED) – a semiconductor diode ranked among the optoelectronic components. The simplest LED diodes are implemented as ordinary p-n semiconductor junctions, which after high enough polarization of forward voltage emit electromagnetic radiation in the visible and infrared light.
Color and wavelength of radiation emitted by LED diodes are closely connected with the semiconductor material from which it was made. Usually they are manufactured from compounds (both binary and multicomponent) of elements III and V of the Periodic Table (for example, GaAs – gallium arsenide, GaP – gallium phosphide, GaAsP – arseno-phosphide gallium with right-doping). Elemental composition of the diode is selected in the way that semiconductor structure obtained in the process will allow the emission of light in the desired spectral range. PN junctions of LED diodes with GaAs are mostly produced with a diffusion technique. It ensures a high quantum efficiency. Group of interconnected diodes are used in various types of displays for example Seven segment.
The division of the LED diodes based on the color of light radiation:
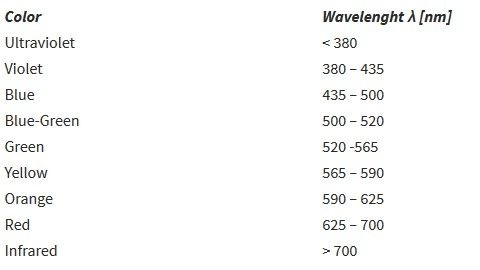
Smooth change of wavelength is accompanied by analogous change in colour. In the table there are only ranges of values in order to improve envision the relation between wavelength and diode colour.
 911electronic.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/charakterystyka3-150x150.jpg 150w" alt="led diode characteristic" width="300" height="300" />
911electronic.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/charakterystyka3-150x150.jpg 150w" alt="led diode characteristic" width="300" height="300" />
The principle of light-emitting diode operation is based on the electroluminescence phenomenon (producing light under the influence of the electric field). Electroluminescence occurs as a result of recombination (annihilation) pair of carriers (electrons and hole) in the area of the PN junction. While electrons flow from higher to a lower energy level, power dissipation occurs in form of heat (non-radiative recombination – at semiconductors with n oblique energy gap) or light (radiative recombination – semiconductors with a simple energy gap). During this flow, electron energy is converted into a quantum of electromagnetic radiation.
The advantages of light-emitting diodes:
the ability to choose light colors,
low voltage (single LED diodes need from 2 to 4V),
low power consumption,
small size element (compared to a standard bulb even very small),
high efficiency,
low energy loss,
durability of the item.
Examples of LED diodes varieties:
RGB LED (Red Green Blue LED) – it has three colors in one box, which allows you to virtually generate any color,
IR (Infrared) – it emits infrared radiation that is used in for example data transmission in older models of mobile phones,
HB LED (High Brightness LED) – diodes with high brightness. They are used in automotive, traffic lights or in streetlights.
Source: 911electronic.com/led-diode-definition-basics-characteristic/




