History:
Mass Spectrometry was discovered by “Denpsten” in 1918.
Introduction:
“It is an analytical technique in which a sample is subjected to electrons from a source, as a result the sample is ionized and these ions have specific m/e ratios which are analyzed through a mass spectrum”
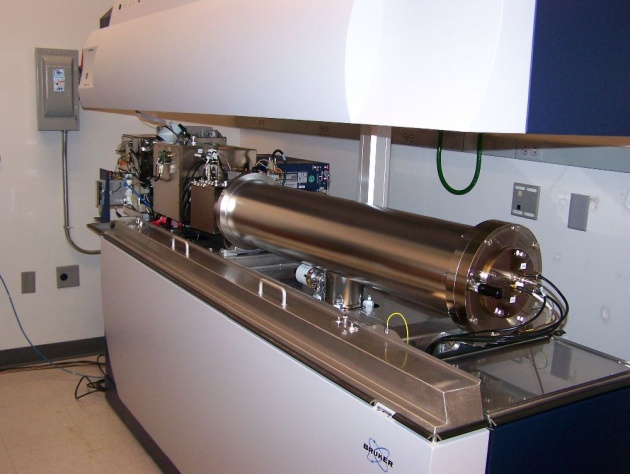

Basic Principle:
In mass spectrometry sample is passed through a vaccum, where electrons from source, leads to the ejection of electrons from the sample, such that:
M à M+ + e-
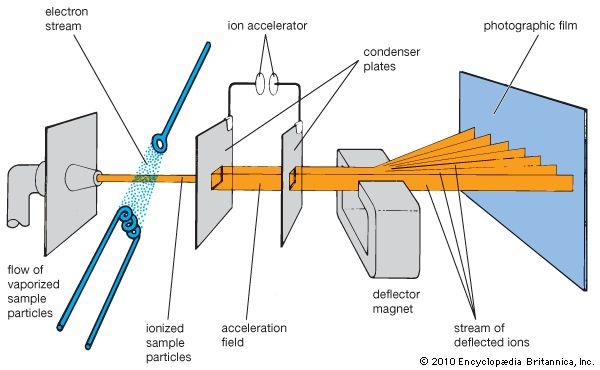
Construction of Mass Spectrometer:
Mass Spectrometer consist of following instrumentations.
1. Inlet System:
In inlet system heating coils are present. Here samples, whose mass spectrum is measured, are evaporated by heating them.
2. Ionization Chambers:
In this chamber ionization of sample is done, mostly by electron gun.

3. Accelerating Systems:
Accelerating system is in the form of linear acceletor , which provides electric field and accelerates the sample towards analyzer.
4. Analyzer:
In analyzer cations are deflected by magnet. Analyzer may be:
· Single focusing magnetic analyzer.
· Double focusing magnetic analyzer.
5. Ion Collector:
Finally cations are reached towards ion collector which is Be-Cu electron multiplier system or photographic films.

6. Detector:
Detectors are used for detection of electric signals. Photographic plate is commonly used detectors.
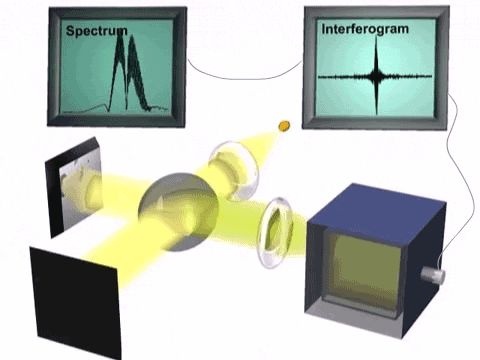
7. Amplifier:
The current from detector is fed into amplifier, which amplifies the current.
Working of mass spectrometry:
Ionization chamber:
The sample is injected as a gas in ionization chamber.
Electron gun:
Electrons come from the electron gun collide with the sample atoms or molecules. As a result of these collisions electrons from the sample atoms are knocked out and they become positive ions.
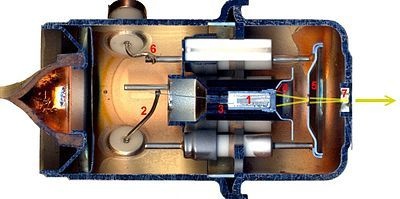
Accelerated System:
The positive ions are accelerated by the electric field and finally reach a region where an electromagnet is applied.
Separation of ions:
Different ions separate on the basis of m/e ratio. In the magnetic field the ions deflect in circular path. Lighter ions (low m/e) deflect to large extent than heavier ions.
Detection:
Ions strikes the detector and electric signals detected and amplified.
In recorder the electric current produce peaks on a chart. Higher is the peak of a species higher is its abundance.
Signal intensity:
The intensity of the electric signal is directly proportional to the number of ions striking the detector.
Mass spectrum:
“Mass spectrum is a chart in which m/e is taken on x-axis and relative abundance is taken on y-axis”.
Molecular ions:
When a molecule is introduced into mass spectrometer, the molecular ion (M+) is produced due to loss of an electron. They are produced when energy of ion source is 9-15ev.
Fragmentation ions:
At energy above 70ev the sample is converted into various fragments.
Applications of Mass Spectrometry:
Mass spectrometry is a useful technique for quantitative and qualitative analysis.

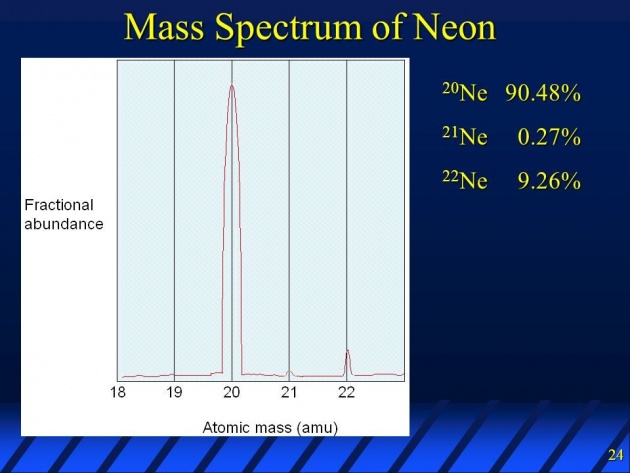
Mass spectrum of neon:
Neon spectrum obtain by its mass spectrometery shows three peaks with m/e equal to 20,21, and 22 which correspond to 20Ne,21Ne and 22Ne. Neon -20 is the most abundant and Neon -21 is the least abundant isotope as clear from the heights of their peaks.
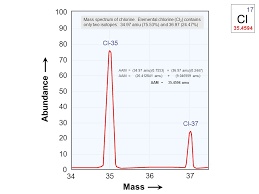
Mass spectrum of Cl:
Mass spectrum of Cl shows 2 isotopes Cl-35 and Cl-37.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
If you want make money on internet then join Film Annex, click on this and register on Film Annex. It provide a great way to express your thoughts and ideas,with other peoples. If you think you are a good writer then write blogs and make money, and if you think you are good movie maker then make movies and make money.
Facebook, Twitter, G mail and mail me on this mailing address (m.arsalanarsalan@ymail.com)
You can view my all blogs, Videos and Microblogs from this link.
Writer: Muhammad Arsalan.