METEROLOGY:
Meteorology is a science of weather and the word “Meteor” means a shooting stars on a visible phenomena occuring in the nature.
TYPES OF METEROLOGY
Hydro Meteor (Water)
Litho Meteor (Stone)
Electro Meteor (Electrical )
Photo Meteor (Light)
HYDRO METEOR
Greek words means WATER
Hydrometeor, any water or ice particles that have formed in the atmosphere or at the Earth’s surface as a result of condensation or sublimation. Water or ice particles blown from the ground into the atmosphere are also classed as hydrometeors. Some well-known hydrometeors are clouds, fog, rain, snow, hail, dew, rime, glaze, blowing snow, and blowing spray.

LITHO METEOR
Greek words means STONE
Atmospheric phenomena which affect the state of the atmosphere. They constitute dry particles that hang suspended in the atmosphere, such as dust, smoke, sand, and haze.

ELECTRO METEOR
Any visible or audible manifestation of atmospheric Electricity, as lightning or thunder.

PHOTO METEOR
Greek words means VISIBLE LIGHT.
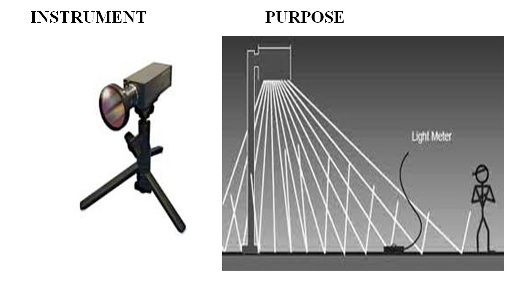
An instrument that measures brightness,
light distribution, color, etc.
ATMOSPHERE
Envelope of gasses surrounding the earth is known as ATMOSPHERE.
75% of the atmosphere lies within 11 Km from the earth surface and 90% of the atmosphere is within 40 Km from the earth’s surface.
Chief constituent of atmosphere is Nitrogen gas which is about 78% by volume and the second big constituent is Oxygen gas which is about 21% by volume and the other gases like Argon and Carbon dioxide etc by 1% by volume. In wet/saturated air water vapors disturb the composition of air up to 5%.
These are the main constituents of lower atmosphere which starts from the surface of the to about 100 kilometers.
Argon 0.93 %
Carbon dioxide 0.03 %
Other gases 0.04 %
Other Gases
(1)Hydrogen (2)Neon (3)Helium
(4)Krypton (5)Xeon (6)Ozone
(7)Radon
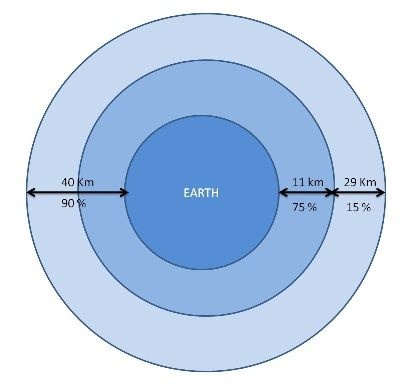
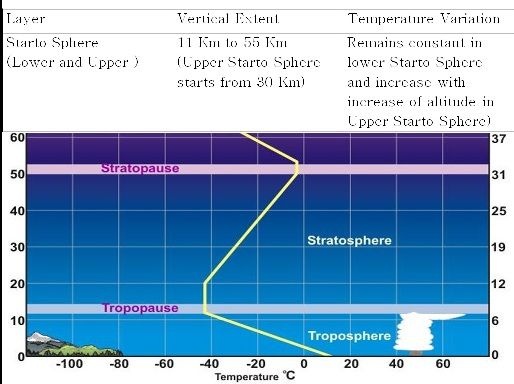
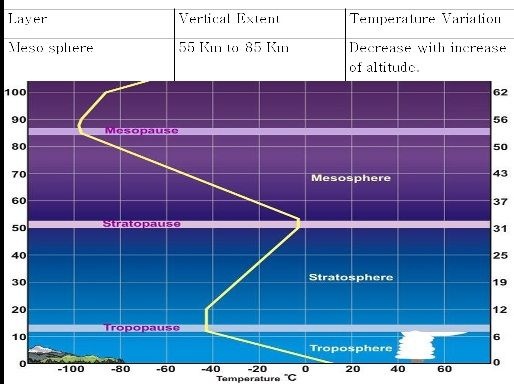
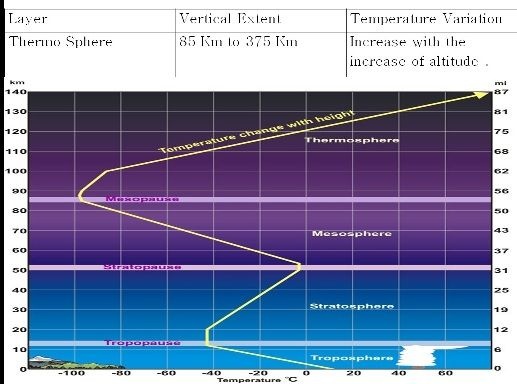
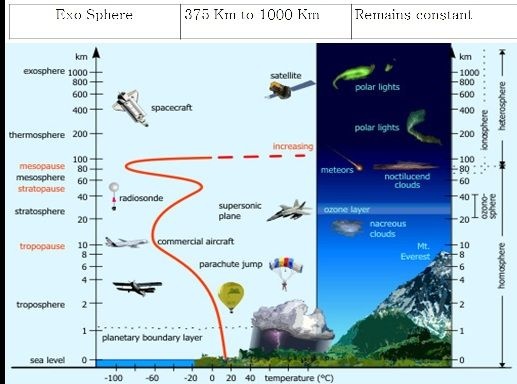
Vertical Division Of Atmosphere
The vertical extent of atmosphere is about 1000 Kilometers from the surface of the earth, depending upon variation in temperature the atmosphere has been divided into six shells or layers as per following table.
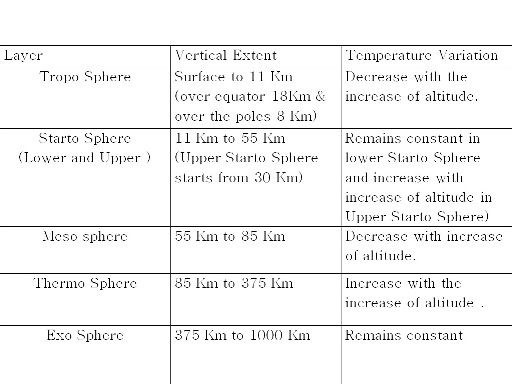
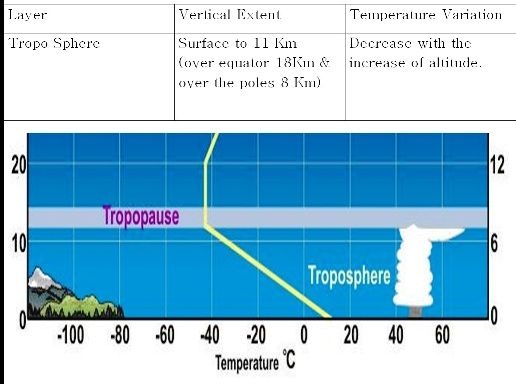
Note:
Condition in which temperature remains constant is knows as Isothermal Condition and condition in which temperature increase with increase of altitude is known as Inversion and condition in which temperature decrease with increase of altitude is known as Positive Laps rate.
(For example lower starto sphere is an isothermal layer where as upper strato sphere is an inversion layer).
Basic Properties of Atmosphere
Following are the four basic properties of the atmosphere.
Temperature
Atmospheric pressure
Air Density
Humidity
Variation in these properties causes formation of weather.
Temperature:
The degree of hotness or coldness of a body or environment.
Celsius (C) = 5/9 (F-32)
Fahrenheit (F) = 9/5 (C+32 )
Kelvin (K)= (C+273.15)
Pressure:
Pressure is defined as force per unit area
Formula :-
P=F/A
Unit :-
Pascal (Pa)
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure is defined as
“The force per unit area exerted against a surface by the weight of the air above that surface.”
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as
“ mass per unit volume”.
The symbol most often used for density is ρ (the lower case Greek letter rho).
Formula :-
ρ=m / V
Unit :-
kg/m3
Air Density
The density of air, is the mass per unit volume of Earth’s atmosphere.
Air density decreases with increasing altitude, as does air pressure. At sea level and at 15°C according to ISA (International Standard Atmosphere), air has a density of approximately 1.225
Humidity
Humidity is a term for the amount of water vapor in the air.
“A quantity representing the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere or a gas.”
ICAO Standard Atmosphere(ISA)
It is the hypothetical atmosphere created by ICAO in which certain standard value of out side Air temperature, Atmospheric Pressure and Air Density at various altitudes usually from -2000ft to 50000ft are assumed.
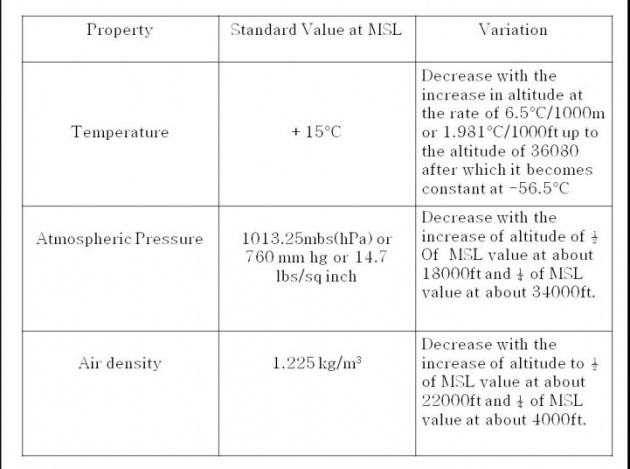
Note :
ISA temperature at a certain pressure altitude can be calculated by the following formula.
ISA=15-(2x P.A)
If OAT is warmer than ISA, then deviation is Positive.
If OAT is colder than ISA, then deviation is Negative.
BAROMETERS
Force per unit area exerted by the weight of air above any given level is known as Atmospheric Pressure, the instrument used for the measurement of this pressure is called BAROMETER.
There are two types of barometers
Mercury Barometer
Aneroid Barometer
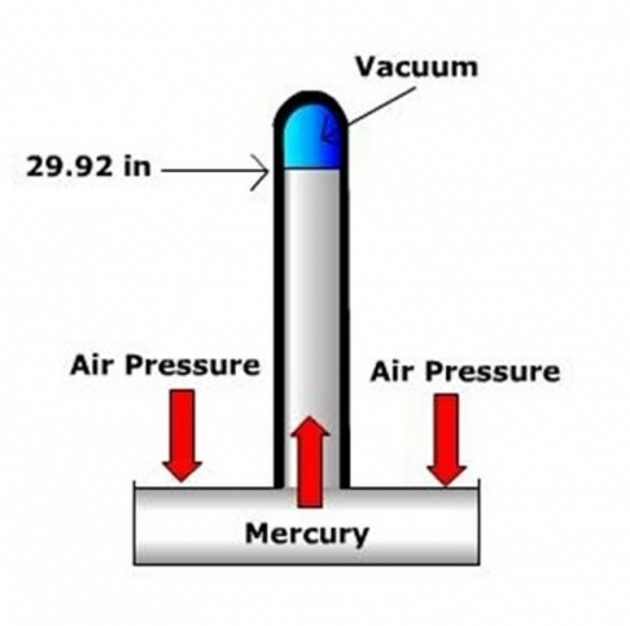
Mercury Barometer
In Mercury Barometer, weight of the mercury coincide the tube above the level of mercury in the cup which is being balanced by the weight of air.
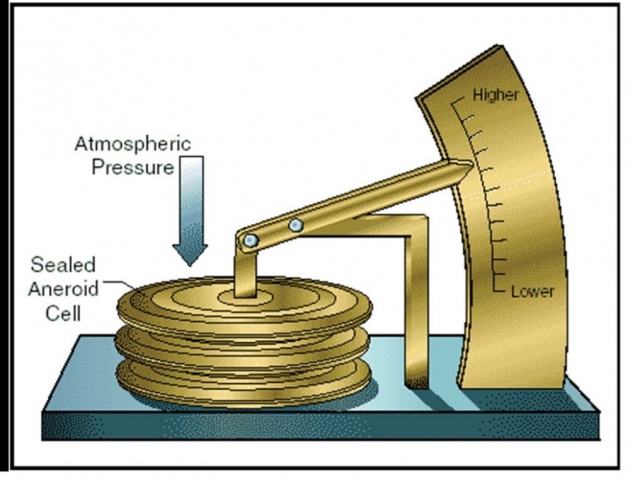
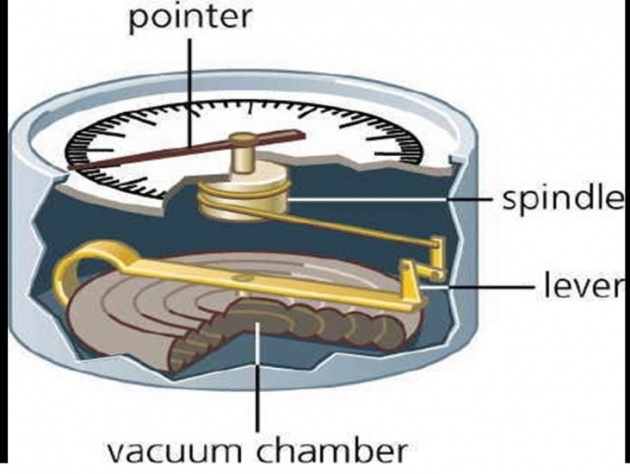
Aneroid Barometer
In Aneroid Barometer, the sensing element is partially evacuated capsule made of flexible material. The changes in the thickness of capsule are magnified by a system of gears and pressure is indicated by a pointer against a calibrated scale.
Pressure
Force per unit area is called Pressure . The metric unit of pressure is Dyne, 1 Dyne is the force required to produce an acceleration of 1cm/sec in a mass of 1gm.
In aviation following three units for measurement of atmospheric pressure are used.
Millibars (mb) or Hecto-pascals (H pa)
Millimeters of Mercury(mm(Hg))
Inches of Mercury (in.(Hg))
100mb.=750.1 mm.=29.53 in.
1mb=1000 dynes/ms2
Variation Of Atmospheric Pressure
There are three types of variations in atmospheric pressure.
Horizontal Variation
Vertical Variation
Diurnal Variation
Horizontal Variation of Pressure
Variation in surface temperature cause variation in atmospheric pressure is generally lower over a warm surface and higher over a cold surface ,and therefore
“the atmospheric pressure is lower in summer and higher in winter.”
Vertical Variation of Pressure
Atmospheric pressure at any level is caused by the weight of air above it and as such atmospheric pressure decrease with the increase in altitude, the relation ship between heights and pressure is n logarithmic proportion.
How ever change of height per Mili bar change of pressure at any level can be calculated by the following formula.
Δh=96T/P
Where Δh is in feet, T Is in degree Kelvin and P is in Hpa or Mbs.
If OAT is 15 degree Centigrade which is equal to 288.15 degree Kelvin ,atmospheric pressure is 1013.25 H Pa, then
Δh=96T/P
Δh=96x288.15/1013.25
Δh=27.3 ft/H Pa
(generally Δh for ISA is taken as 30ft/H Pa)
Diurnal Variation of Pressure
In undistributed weather conditions the atmospheric pressure show two maxima and minima, being highest at 1000 and 2200 hours LMT and being lowest at 0400 and 1600 hours LMT.
Diurnal variation of pressure is highest in the equatorial areas and decrease with the increase of latitude, being negligible in the polar areas.
(Note: Diurnal variation means daily variation in the pressure)
Factor Affecting Surface Temperature
Factors that effect surface temperature are time of the day, season of the year, latitude, nature of terrain, distance from sea and prevailing winds.
Altimetry (Q Codes for Pressure)
Following are the Q codes used for pressure.
- QFE
- QNH
- QNE
- QFF
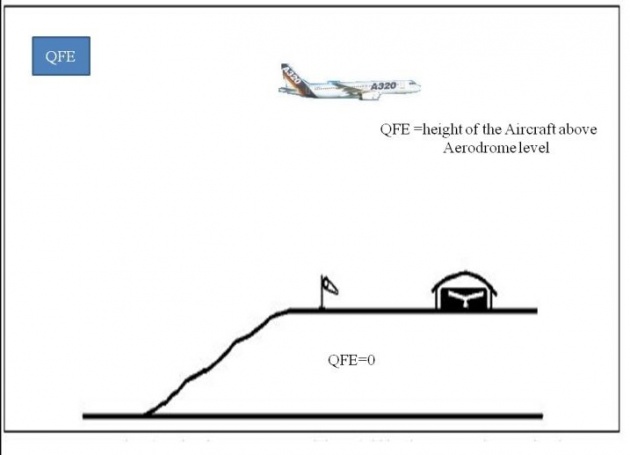
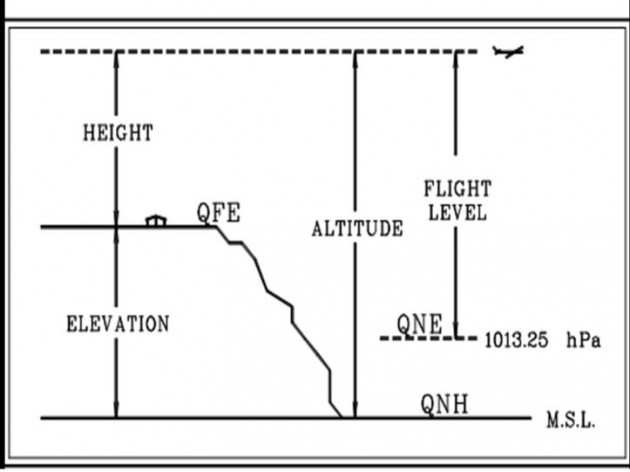
QFE
Observed atmospheric pressure at the station. When QFE is set on the altimeter subscale on ground it indicates zero and in the air it indicates height of the aircraft above aerodrome level.
QNH
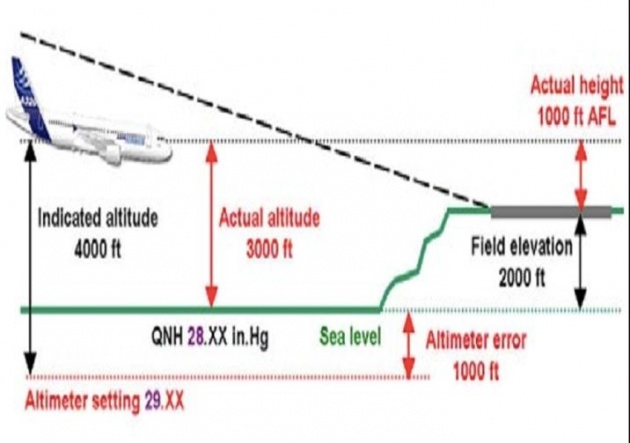
QFE or station level pressure reduced to mean sea level in accordance with the standard atmosphere. When QNH is set on the altimeter subscale on ground it indicate the elevation of aerodrome and in the air it indicates the altitude of an aircraft above mean sea level.
QNE
It is standard mean sea level pressure (1013.25H Pa or 29.29 inches Hg).When QNE is set on the altimeter subscale on ground it indicate the pressure altitude of the airport and in air it indicates the pressure altitude of the aircraft.
QFF
QFE or station level pressure reduced to mean sea level according to meteorological formula, QFF is not used for altimeter setting it is used for plotting atmospheric pressure on meteorological charts.
Note : QFF ≠ QNH, in words QFF is not Equals to QNH.



