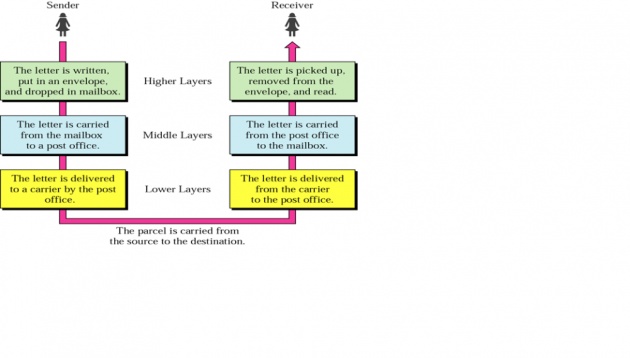
Layered Model: Sending a Letter
 OSI Model
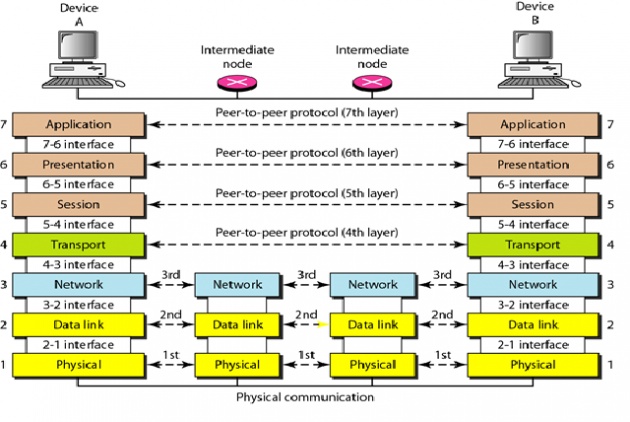
OSI Model
ISO is the organization. OSI is the model
Open Systems Interconnection
Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
Seven layers
¨ Each layer performs a subset of the required communication functions
¨ Each layer relies on the next lower layer to perform more primitive functions
¨ Each layer provides services to the next higher layer
¨ Changes in one layer should not require changes in other layers
Interaction between layers in the OSI model
Layer and interface
Physical Layer
The physical layer is responsible for movements of individual bits from one hop (node) to the next
¨ Mechanical: Relates to physical properties of interface to transmission medium. E.g. pluggable connector that joins circuits
¨ Electrical: Relates to representation of bits and data transmission rate of bits.
¨ Functional: specifies the functions of individual circuits of physical interface between a system and transmission medium.
¨ Procedural: specifies sequence of events by which bit streams are exchanged across physical medium

Physical Layer: Duties
Physical characteristics of interfaces and media
Representation of bits
Data rate
Synchronization of bits
Line configuration
Physical topology
Transmission mode
Data Link Layer
The data link layer is responsible for moving frames from one hop (node) to the next
Transform the physical layer to a reliable (error-free) link

Data Link Layer: Duties
Framing
Physical addressing
Flow control
Error control
Access control
Network Layer
The network layer is responsible for the delivery of packets from the source host to the destination host
¨ Higher layers do not need to know about underlying technology
¨ Computer systems engage in dialogue with network to specify destination address and request network facilities.
¨ Not needed on direct links
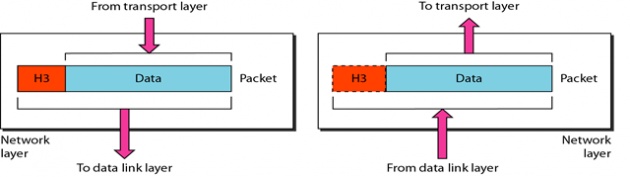
Network Layer: Duties
Logical addressing and routing
Transport Layer
The transport layer is responsible for delivery of a message from one process to another
Transport Layer: Duties
Service-point (port) addressing
Segmentation and reassembly
Connection control
Flow control
Error control
Session Layer
Session layer is responsible for dialog control and synchronization
Presentation Layer
Presentation layer is responsible for translation, compression, and encryption
Application Layer
Application layer is responsible for providing services to the user
Application Layer: Services
Network virtual terminal
Mail services
File transfer, access, and management
Directory services
Summary of Layers




