The waste products of the body are excreted through the lungs, the skin, the intestines, and the kidneys. The liver also excretes waste products-the bile, pigments and cholesterol.
The lungs eliminate water and carbon dioxide through the expired air. The skin eliminates water in the form of perspiration. Included in the perspiration are small amounts of inorganic and organic salts. The feces, excreted from the large intestine, contains undigested and undigestible material plus the excretory products from the liver- the bile pigments and cholesterol-some water, some organic and inorganic salts. The primary excretory organs of the body, however, are the kidneys, which excrete water and water-soluble compounds including nitrogen compounds from the catabolisms of amino acids.
The kidneys are important not only for their excretory function but also because of their role in the control and regulation of water, electrolyte, and acid-base balances in the body.
What Are the Warning Signs of Kidney Disease?
Kidney disease usually affects both kidneys. If the kidneys' ability to filter the blood is seriously damaged by disease, wastes and excess fluid may build up in the body. Although many forms of kidney disease do not produce symptoms until late in the course of the disease, there are six warning signs of kidney disease:*High blood pressure.
*Blood and/or protein in the urine.
*A creatinine and Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) blood test, outside the normal range. BUN and creatinine are waste that build up in your blood when your kidney function is reduced.
*A glomerular filtration rate (GFR) less than 60. GFR is a measure of kidney function.
*More frequent urination, particularly at night; difficult or painful urination.
*Puffiness around eyes, swelling of hands and feet.
-Read more: National Kidney Foundation-
Reference: Science Daily
Normal Constituents
Approximately 50 to 60 gram of dissolved solid material is excreted daily in the urine of the average person. This solid material has both organic and inorganic constituents. The inorganic constituents of urine make up approximately 45 percent of the total solids; the organic constituents compose the other 53 percent.
Organic Constituents
Urea
The principal end product of the metabolism of protein, urea, comprises about one-half of the total solids in the urine.
Uric Acid
Uric acid, a product of the metabolism of purines from nucleoprotein, is only slightly soluble in the water and is excreted primarily as urate salts.
When urine is allowed to stand, uric acid may be crystallized and settle out since it is only slightly soluble in water or acid solution.
The average daily excretion of uric acid is about 0.7 g, but an increase in nucleoproteins in the diet will cause an increase excretion of uric acid. The output or uric acid is also increased in leukemia, in severe liver disease, and in various stages of gout. Deposits or urates and uric acid in the joints and tissues are also characteristic of gout, so this disease appears to be a form of arthritis.
Under certain conditions, uric acid or urates crystallize in the kidneys and are called kidney stones, or calculi. Kidney stones can also be formed from calcium oxalate.
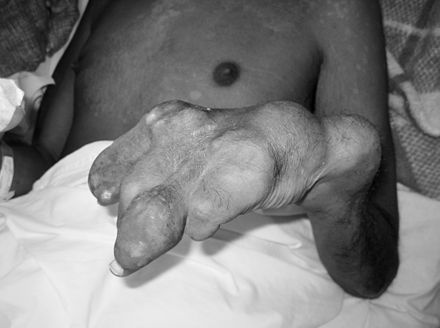
The ravaging effects of gout are manifest in the deformed hands of a patient afflicted with this crippling disease.
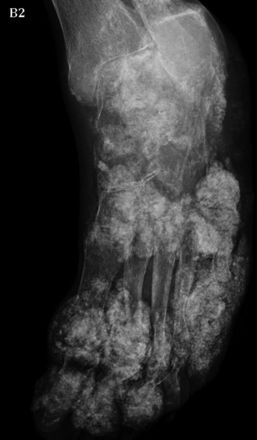
Gout affects the left foot through radiography that shows severe. Doctors found out mutation of the renal urate function.
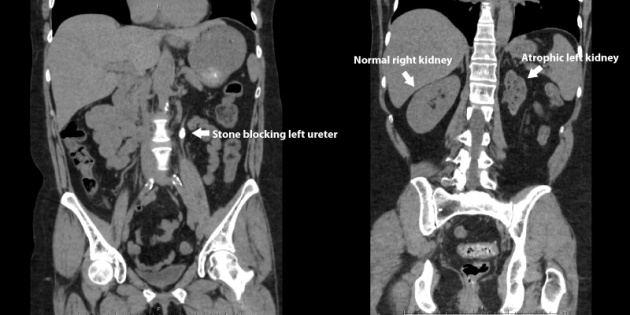
The CT scan shows the difference between normal and abnormal kidneys and determined the appearance of the stone which is abnormal. The left kidney is atrophied. Some patients may not notice the early signs.
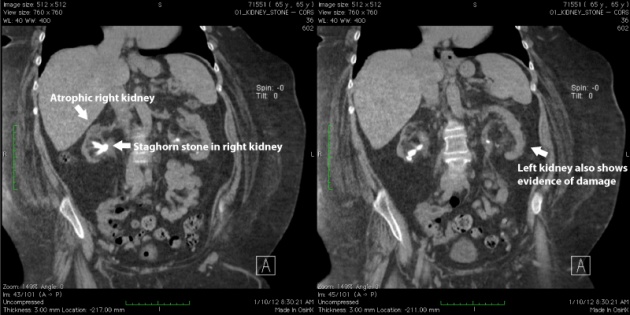
There is a large kidney stone seen in the image that is infected. The patient has also stone in the left that causes to encounter severe back pain on left side.
Creatinine
Creatinine is a product of a breakdown of creatine. The amount of creatine excreted per day is fairly constant regardless of the protein intake. The number of milligrams of creatinine excreted in the urine within 24-hr period per kilogram of the body weight of the creatinine coefficient of the individual. The creatine coefficient in the same period of time. Formation of creatinine appears necessary for the excretion of most of the creatinine.
Creatine
Creatine if produced in the body of the three amino acids: arginine, methionine, and glycine. Creatine is normally present in the muscle, brain, and blood, both as free creatine and as creatine phosphate. Recall the reaction
creatine phosphate+ ADP------> creatine + ATP
Creatinuria is a condition in which abnormal amounts of creatine occurs in the urine. It may occur during starvation, diabetes mellitus, prolonged fevers, wasting diseases, and hypothyroidism. Creatinuria may also occur in pregnancy.
Other Organic Constituents
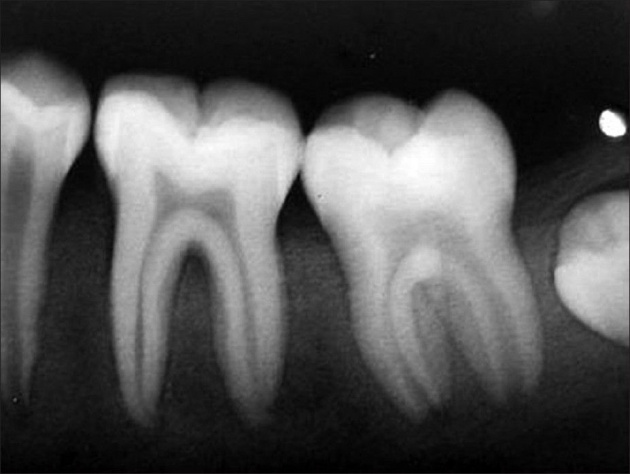
The patient with hyperparathyroidism experienced severe loss of LD (lamina dura) as shown in the IOPA radiograph. The jaw bones' shape has mutated into ground glass which is very typical. The result is caused by the gigantic cell called granulomas. It is a brown tumor.
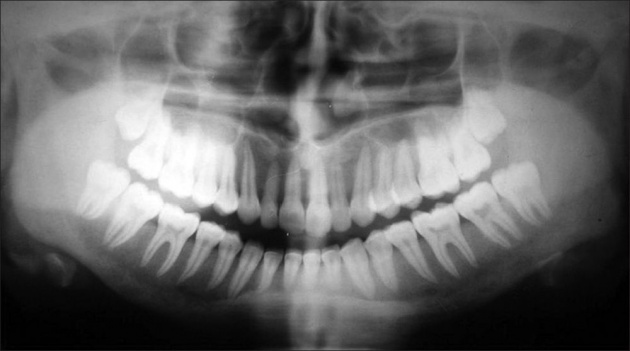
The orthopantomogram results with a very limited wideness of mandible. Patient is also experiencing limited width of the ground glass.
Also present in small amounts are amino acids, Allantoin (from partial oxidation of uric acid), hippuric acid, urobilin, urobilinogen, and biliverdin. The presence of cAMP helps diagnose parathyroid function. Patients with hyperparathyroidism excrete significantly more cAMP and those with hypoparathyroidism excrete significantly less cAMP than persons with normal parathyroid glands.
Urobilinogen excretion is increased in hemolytic anemias and in liver disease. Biliverdin excretion is increased in certain liver and biliary diseases.
Tests for pregnancy are based on the fact that the implantation of a fertilized ovum in the placental tissue produces the hormone chorionic gonadotrophin, which is excreted in the urine. Tests for the presence of chorionic gonadotropin (for pregnancy) are based on the fact that this hormone will react with specific antibodies and can yield a result in the physician's office or at home in a very short time.
In addition to these constituents, the urine also normally contains very small amounts of vitamins, other hormones, and enzymes. Urinalysis for these substances is of diagnostic value.
References:
- http://csmbio.csm.jmu.edu/biology/danie2jc/urinalysis.htm
- https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-ap/chapter/urine/
Inorganic Constituents
The inorganic constituents of urine area are the various positive and negative ions that make up the inorganic compounds being excreted. Among these are the following.
Chloride Ions
Between 9 and 10 g of chloride ion excreted daily, mostly as sodium chloride. The amount of chloride ion varies with the intake, which is primarily sodium chloride. The excretion of sodium chloride is decreased in fevers and in some stages of the nephritis.
Courtesy of the video: Health Apta via Youtube
Sodium Ions
The amount of sodium ion excreted varies with the intake and the body's requirement. However, it is usually about 4 g per day.
Phosphates
The amount of phosphates present in the urine also depends upon the diet; the amount is higher when the diet contains food high in phosphorus (nucleoproteins and phospholipids). An increase in excreted phosphates is found in certain bone disease and in hyperparathyroidism. A decrease in phosphates is found in hypoparathyroidism, in renal disease, and during pregnancy.
Sulfates
The sulfates in the urine are derived from the metabolism of sulfur-containing-proteins, so the amount of sulfur is influenced by the diet. Sulfates are found as both organic and inorganic salts.
Ammonium Ions
The hydrolysis of urea produces such ammonium compounds of chlorides, sulfates, and phosphates in the urine.
Other Ions
In addition to the sodium and ammonium ions, other positive ions present in the urine are calcium, potassium, and magnesium.
The amount of calcium ions in the urine is increased by hyperthyroidism and osteoporosis and decreased in hypoparathyroidism and vitamin D deficiency.
Nitrite ions in the urine indicate a decreasing of bacteria in the urinary tract.
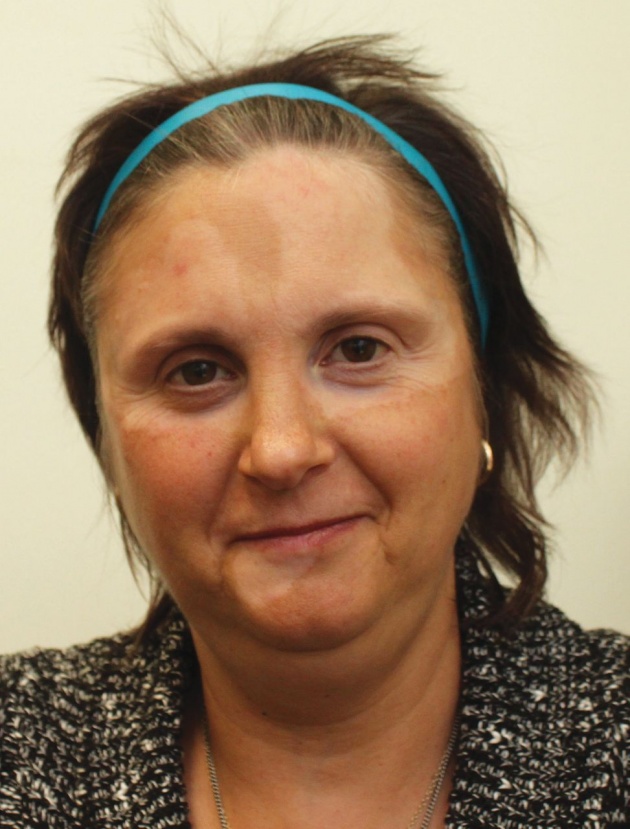

The patient struggles vitiligo on skin face as one of the Addison's disease symptoms. The diagnosis revealed an acute stage after months of investigating gastrointestinal cases.

The patient's hands are also in the background of vitiligo. Patient's urine was seen with increased of sodium to potassium.
The normal ratio of sodium to potassium in the urine is 2 parts sodium to 1 part potassium. The ratio of sodium to potassium is increased to Addison's disease.
Magnesium concentration in the urine is decreased in chronic alcoholism.
Abnormal Constituents
Because proteins are colloids and because colloids cannot pass through membranes, urines should not normally contain protein. Proteinuria denotes the presence of protein in the urine. Sometimes it is called albuminuria because albumin is the smallest plasma protein and is protein most frequently found in the urine. In cases of kidney disease, such as nephritis and nephrosis, and in severe heart disease, the protein appears in the urine. The presence of the urine resulting in such disorders is frequently called renal proteinuria or renal albuminuria to distinguish it from false albuminuria, which is a temporary harmless condition. False albuminuria, often called orthostatic albuminuria, is found in certain patients who stand for a long period of time. It is caused by the constriction of the kidney's blood vessels and disappears when the patient lies down. Small amounts of protein may also be found in the urine after severe muscular exercise, but soon they disappear.
The tests for the presence of the protein in the urine is heated, any protein coagulates when heated. When a sample or urine is heated, any protein (albumin) present will precipitate out as a white cloud. However, phosphates may also precipitate when the urine is heated. To prove that the cloudy substance is albumin, the urine, after heating, is acidified with dilute acetic acid. The acid will dissolve the phosphates but not the protein, so a cloudy precipitate in the urine after heating and acidification is a verification of the presence of protein.
Glucose
The presence of glucose in the urine is called glycosuria. Normally there is a very small amount of glucose present in the urine, but this amount is too small to get a positive result when in urine is tested in Benedict's solution. Glucose may be found in the urine after severe muscular exercise, but this condition clears up when the body returns to normal. Glucose may also be found in the urine after a meal high in carbohydrates. Glycosuria may be caused by such diseases as diabetes mellitus or renal diabetes or to liver damage.
Other Sugars
Lactose and galactose may occur in the urine during pregnancy and lactation. Both of these sugars give a positive result to Benedict's test. Pentoses may occur in the urine after consumption of foods such as plums, grapes, and cherries, which contain large amounts of these carbohydrates.
Ketone Bodies
Ketone (acetone) bodies are present in the urine during diabetes mellitus, in starvation, or in other circumstances with inadequate carbohydrate intake. Such a condition is termed ketonuria. The excretion of the ketone bodies, which are acidic compounds, requires alkaline compounds. This results in a depletion of the alkaline reserved on the blood and leads to acidoses. The kidneys produce more ammonia to neutralize these ketone bodies.
The test for the presence of ketone bodies in the urine is performed by adding sodium nitroprusside to a sample of urine and then making the mixture alkaline with ammonium hydroxide. The presence of ketone bodies is indicated by a pink-red color. Normal urine gives no color with this test.
Blood
The presence of blood in the urine is called hematuria. It may result from lesions or stones in the kidneys or urinary tract. The presence of free hemoglobin in the urine, hemoglobinuria, results from hemolysis of the red blood cells caused by an injection of a hypotonic solution, severe burns, or blackwater fever.
Large amounts of blood in the urine can be detected by reddish color. Small amounts do not color urine enough to show any color change but can be detected by the use of the test dipstick.
Urinalysis
The health care professional can test the urine in the office using a dipstick or can send it out to a lab for analysis. Sometimes urine tests using a dipstick can be positive even though the patient has no blood in the urine, which results in a “false-positive” test. The health care professional may look for red blood cells by examining the urine under a microscope before ordering further tests.Prior to obtaining a urine sample, the health care professional may ask a woman when she last menstruated. Sometimes blood from a woman’s menstrual period can get into her urine sample and can result in a false-positive test for hematuria. The test should be repeated after the woman stops menstruating.
-Read more: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases-
Bile
Normally, bile is excreted by the liver into the small intestine and eventually ends up in the feces. The presence of bile in the urine indicates an obstruction to the flow of bile to the intestines. Bile in the urine is indicated by a greenish brown color. Bile in the urine is also indicated by the presence of yellow foam when the urine is shaken.
Phenylpyruvic Acid
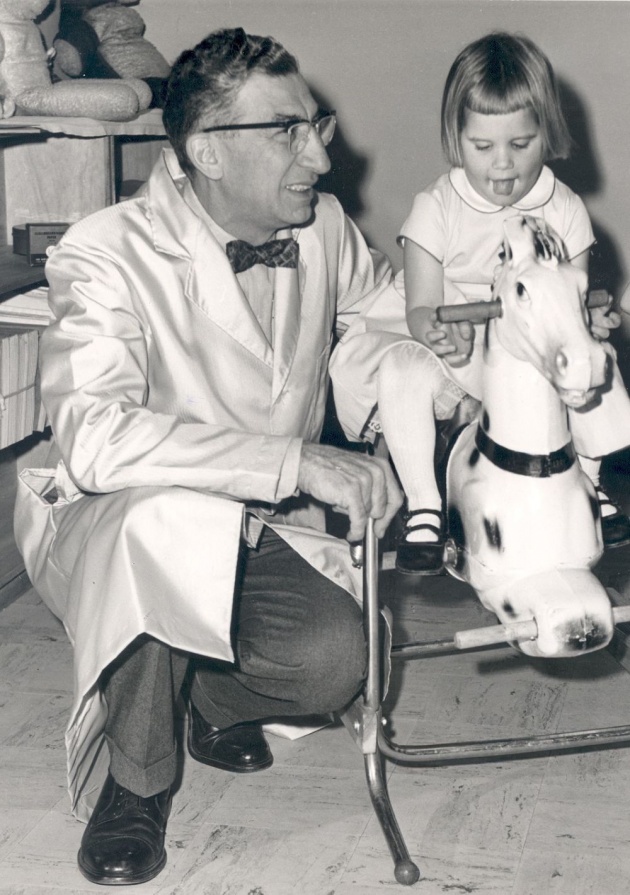

A patient with phenylketonuria (right) was diagnosed after two weeks of birth. Doctor Harry Wiseman (left) prescribed more phenylalanine to her diet.
Phenylpyrivic acid, an intermediate product in the metabolism of the essential amino acid phenylalanine, is not normally present in the urine. However, its presence can be detected in the urine of a person with phenylketonuria (PKU). If this disease is not detected and treated early, mental retardation results. For this reason, some states require screening of newborns for this disease.
Bilirubin
Bilirubin is present in the urine of patients with conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Such patients are said to have choluric jaundice. Such a condition can be caused by (a) Dubin-Johnson syndrome, which is caused by a genetic defect in the hepatic secretion of bilirubin into the bile, or (b) biliary tree obstruction because of a blocking of the hepatic or common bile ducts.
Urobilinogen

Even the newborn babies can be affected with Jaundice. Mothers are encouraged to breastfeed to fight the suspected disease.
Increased levels of urobilinogen and the absence of biliverdin in the urine is an indication of hemolytic jaundice. In addition, increased levels of urobilinogen can indicate pernicious anemia.
Creatine
Normally small amounts of creatine are present in the urine. Elevated levels of this compound can indicate muscular dystrophy, myasthenia gravis, muscle wasting poliomyelitis, or hyperthyroidism.
Uric Acid
Elevated levels of uric acid can indicate gout, Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, and some cases of glycogen storage disease. Decreased levels can indicate renal insufficiency.
Courtesy of the video: Dr. G. Bhanu Prakash via Youtube
References:
- https://labmonk.com/performing-test-for-normal-inorganic-and-organic-constituents-of-urine
- http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/sites/default/files/lab1_11.pdf
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
All rights reserved 2019. No part of this article
may be reproduced without special credits
in writing from the publishers of the following websites resourced above.