Photography is the science, art and practice of creating durable images by recording light or other electromagnetic radiation, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such asphotographic film.[1]
Typically, a lens is used to focus the light reflected or emitted from objects into a real image on the light-sensitive surface inside a camera during a timed exposure. With an electronic image sensor, this produces an electrical charge at each pixel, which iselectronically processed and stored in a digital image file for subsequent display or processing. The result with photographic emulsion is an invisible latent image, which is later chemically "developed" into a visible image, either negative or positivedepending on the purpose of the photographic material and the method ofprocessing. A negative image on film is traditionally used to photographically create a positive image on a paper base, known as a print, either by using an enlarger or by contact printing.
Photography is employed in many fields of science, manufacturing (e.g.,photolithography) and business, as well as its more direct uses for art, film and video production, recreational purposes, hobby, and mass communication.
Etymology[edit]
The word "photography" was created from the Greek roots φωτός (phōtos), genitive of φῶς (phōs), "light"[2] and γραφή (graphé) "representation by means of lines" or "drawing",[3] together meaning "drawing with light".[4]
Several people may have coined the same new term from these roots independently. Hercules Florence, a French painter and inventor living in Campinas, Brazil, used the French form of the word, photographie, in private notes which a Brazilian photography historian believes were written in 1834.[5] Johann von Maedler, a Berlin astronomer, is credited in a 1932 German history of photography as having used it in an article published on 25 February 1839 in the German newspaperVossische Zeitung.[6] Both of these claims are now widely reported but apparently neither has ever been independently confirmed as beyond reasonable doubt. Credit has traditionally been given to Sir John Herschel both for coining the word and for introducing it to the public. His uses of it in private correspondence prior to 25 February 1839 and at his Royal Society lecture on the subject in London on 14 March 1839 have long been amply documented and accepted as settled facts.

Precursor technologies[edit]
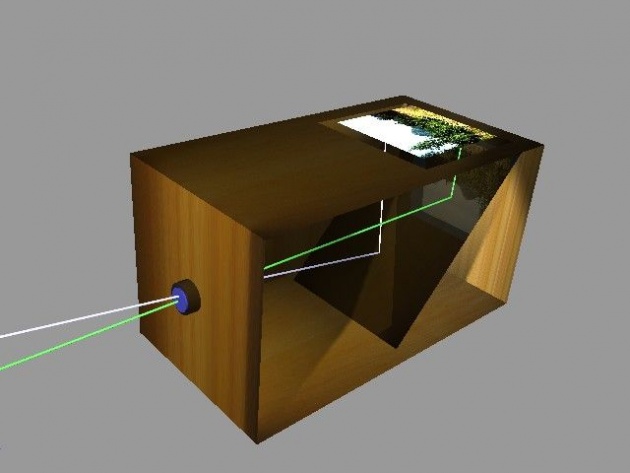
A camera obscura used for drawing images
Photography is the result of combining several technical discoveries. Long before the first photographs were made, Chinese philosopher Mo Di and Greek mathematicians Aristotle and Euclid described a pinhole camera in the 5th and 4th centuries BCE.[7][8] In the 6th century CE, Byzantine mathematician Anthemius of Tralles used a type of camera obscura in his experiments,[9] Ibn al-Haytham(Alhazen) (965–1040) studied the camera obscura and pinhole camera,[8][10]Albertus Magnus (1193–1280) discovered silver nitrate,[11] and Georg Fabricius(1516–71) discovered silver chloride.[12] Techniques described in the Book of Opticsare capable of producing primitive photographs using medieval materials.[13][14][15]
Daniele Barbaro described a diaphragm in 1566.[16] Wilhelm Homberg described how light darkened some chemicals (photochemical effect) in 1694.[17] The fiction book Giphantie, published in 1760, by French author Tiphaigne de la Roche, described what can be interpreted as photography.[16]
The discovery of the camera obscura that provides an image of a scene dates back to ancient China. Leonardo da Vincimentions natural camerae obscurae that are formed by dark caves on the edge of a sunlit valley. A hole in the cave wall will act as a pinhole camera and project a laterally reversed, upside down image on a piece of paper. So the birth of photography was primarily concerned with inventing means to fix and retain the image produced by the camera obscura.
Renaissance painters used the camera obscura which, in fact, gives the optical rendering in color that dominates Western Art. The camera obscura literally means "dark chamber" in Latin. It is a box with a hole in it which allows light to go through and create an image onto the piece of paper.

Around the year 1800, Thomas Wedgwood made the first known attempt to capture the image in a camera obscura by means of a light-sensitive substance. He used paper or white leather treated with silver nitrate. Although he succeeded in capturing the shadows of objects placed on the surface in direct sunlight, and even made shadow-copies of paintings on glass, it was reported in 1802 that "the images formed by means of a camera obscura have been found too faint to produce, in any moderate time, an effect upon the nitrate of silver." The shadow images eventually darkened all over.[19]
The first permanent photoetching was an image produced in 1822 by the Frenchinventor Nicéphore Niépce, but it was destroyed in a later attempt to make prints from it.[18] Niépce was successful again in 1825. In 1826 or 1827, he made theView from the Window at Le Gras, the earliest surviving photograph from nature (i.e., of the image of a real-world scene, as formed in a camera obscura by alens).[20]
World's earliest surviving camera photograph, 1826 or 1827: View from the Window at Le Gras
Because Niépce's camera photographs required an extremely long exposure (at least eight hours and probably several days), he sought to greatly improve hisbitumen process or replace it with one that was more practical. In partnership withLouis Daguerre, he worked out post-exposure processing methods that produced visually superior results and replaced the bitumen with a more light-sensitive resin, but hours of exposure in the camera were still required. With an eye to eventual commercial exploitation, the partners opted for total secrecy.
Niépce died in 1833 and Daguerre then redirected the experiments toward the light-sensitive silver halides, which Niépce had abandoned many years earlier because of his inability to make the images he captured with them light-fast and permanent. Daguerre's efforts culminated in what would later be named the daguerreotypeprocess, the essential elements of which were in place in 1837. The required exposure time was measured in minutes instead of hours. Daguerre took the earliest confirmed photograph of a person in 1838 while capturing a view of a Paris street: unlike the other pedestrian and horse-drawn traffic on the busy boulevard, which appears deserted, one man having his boots polished stood sufficiently still throughout the approximately ten-minute-long exposure to be visible. The existence of Daguerre's process was publicly announced, without details, on 7 January 1839. The news created an international sensation. France soon agreed to pay Daguerre a pension in exchange for the right to present his invention to the world as the gift of France, which occurred when complete working instructions were unveiled on 19 August 1839.


Meanwhile, in Brazil, Hercules Florence had apparently started working out a silver-salt-based paper process in 1832, later naming it Photographie, and an English inventor, William Fox Talbot, succeeded in making crude but reasonably light-fast silver images on paper as early as 1834 but had kept his work secret. After reading about Daguerre's invention in January 1839, Talbot published his method and set about improving on it. At first, like other pre-daguerreotype processes, Talbot's paper-based photography typically required hours-long exposures in the camera, but in 1840 he created the calotype process, with exposures comparable to the daguerreotype. In both its original and calotype forms, Talbot's process, unlike Daguerre's, created a translucent negative which could be used to print multiple positive copies, the basis of most chemical photography up to the present day. Daguerreotypes could only be replicated by rephotographing them with a camera.[21]Talbot's famous tiny paper negative of the Oriel window in Lacock Abbey, one of a number of camera photographs he made in the summer of 1835, may be the oldest camera negative in existence.[22][23]
John Herschel made many contributions to the new field. He invented the cyanotypeprocess, later familiar as the "blueprint". He was the first to use the terms "photography", "negative" and "positive". He had discovered in 1819 that sodium thiosulphate was a solvent of silver halides, and in 1839 he informed Talbot (and, indirectly, Daguerre) that it could be used to "fix" silver-halide-based photographs and make them completely light-fast. He made the first glass negative in late 1839.
In the March 1851 issue of The Chemist, Frederick Scott Archer published his wet plate collodion process. It became the most widely used photographic medium until the gelatin dry plate, introduced in the 1870s, eventually replaced it. There are three subsets to the collodion process; the Ambrotype (a positive image on glass), the Ferrotype or Tintype (a positive image on metal) and the glass negative, which was used to make positive prints on albumen or salted paper.
Many advances in photographic glass plates and printing were made during the rest of the 19th century. In 1891, Gabriel Lippmann introduced a process for making natural-color photographs based on the optical phenomenon of the interferenceof light waves. His scientifically elegant and important but ultimately impractical invention earned him the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1908.
Glass plates were the medium for most original camera photography from the late 1850s until the general introduction of flexible plastic films during the 1890s. Although the convenience of film greatly popularized amateur photography, early films were somewhat more expensive and of markedly lower optical quality than their glass plate equivalents, and until the late 1910s they were not available in the large formats preferred by most professional photographers, so the new medium did not immediately or completely replace the old. Because of the superior dimensional stability of glass, the use of plates for some scientific applications, such as astrophotography, continued into the 1990s, and in the niche field of laser holographyit has persisted into the 2010s.

Hurter and Driffield began pioneering work on the light sensitivity of photographic emulsions in 1876. Their work enabled the first quantitative measure of film speed to be devised.
The first flexible photographic roll film was marketed by George Eastman in 1885, but this original "film" was actually a coating on a paper base. As part of the processing, the image-bearing layer was stripped from the paper and transferred to a hardened gelatin support. The first transparent plastic roll film followed in 1889. It was made from highly flammable nitrocellulose ("celluloid"), now usually called "nitrate film".
Although cellulose acetate or "safety film" had been introduced by Kodak in 1908,[24] at first it found only a few special applications as an alternative to the hazardous nitrate film, which had the advantages of being considerably tougher, slightly more transparent, and cheaper. The changeover was not completed for X-ray films until 1933, and although safety film was always used for 16 mm and 8 mm home movies, nitrate film remained standard for theatrical 35 mm motion pictures until it was finally discontinued in 1951.
Films remained the dominant form of photography until the early 21st century, when advances in digital photography drew consumers to digital formats.[25] Although modern photography is dominated by digital users, film continues to be used by enthusiasts and professional photographers. The distinctively "look" of film based photographs compared to digital images is likely due to a combination of factors, including: (1) differences in spectral and tonal sensitivity (S-shaped density-to-exposure (H&D curve) with film vs. linear response curve for digital CCD sensors [26] (2) resolution and (3) continuity of tone.[27]

Originally, all photography was monochrome, or black-and-white. Even after color film was readily available, black-and-white photography continued to dominate for decades, due to its lower cost and its "classic" photographic look. The tones and contrast between light and dark areas define black-and-white photography.[28] It is important to note that monochromatic pictures are not necessarily composed of pure blacks, whites, and intermediate shades of gray, but can involve shades of one particular hue depending on the process. The cyanotype process, for example, produces an image composed of blue tones. The albumen print process, first used more than 160 years ago, produces brownish tones.
Many photographers continue to produce some monochrome images, sometimes because of the established archival permanence of well-processed silver-halide-based materials. Some full-color digital images are processed using a variety of techniques to create black-and-white results, and some manufacturers produce digital cameras that exclusively shoot monochrome. Monochrome printing or electronic display can be used to salvage certain photographs taken in color which are unsatisfactory in their original form; sometimes when presented as black-and-white or single-color-toned images they are found to be more effective. Although color photography has long predominated, monochrome images are still produced, mostly for artistic reasons. Almost all digital cameras have an option to shoot in monochrome, and almost all image editing software can combine or selectively discard RGB color channels to produce a monochrome image from one shot in color.

Color photography is photography that uses media capable of reproducing colors. By contrast, black-and-white (monochrome) photography records only a single channel of luminance (brightness) and uses media capable only of showing shades of gray.
In color photography, electronic sensors or light-sensitive chemicals record color information at the time of exposure. This is usually done by analyzing the spectrum of colors into three channels of information, one dominated by red, another by green and the third by blue, in imitation of the way the normal human eye senses color. The recorded information is then used to reproduce the original colors by mixing various proportions of red, green and blue light (RGB color, used by video displays, digital projectors and some historical photographic processes), or by using dyes or pigments to remove various proportions of the red, green and blue which are present in white light (CMY color, used for prints on paper and transparencies on film).
Monochrome images which have been "colorized" by tinting selected areas by hand or mechanically or with the aid of a computer are "colored photographs," not "color photographs." Their colors are not dependent on the actual colors of the objects photographed and may be very inaccurate or completely arbitrary.
Color photography has been the dominant form of photography since the 1970s, with monochrome photography mostly relegated to niche markets such as art photography.



