Radio (Part 3 Final)
In previous lecture we have study about the Radio. Radio is a device with the help of which we can hear the voice which is broadcast form the different broadcast channels. In today’s lecture we will discussed about the ionosphere.
THE IONOSPHERE
The ionosphere is having very important and plays different useful role in this universe. It is helpful to protect us from sun’s harmful radiations and also helpful for the radio communication. It influences radio propagation to distant places on the Earth.. The ionosphere is the atmosphere that is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important part in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere.
Radio waves, Like light waves, travel in a straight line. So, unless they were reflected, they would travel straight out into space from the transmitting aerial. Listeners out of sight of the aerial would not receive its radio signals. Fortunately, most radio waves are reflected from electrically charged ‘layers’ between 80 and 500 km up in the Earth’s atmosphere. This region is called the ionosphere because it consists mainly of ions or electrically charged atoms. Short waves are reflected back more strongly than longer waves and so short wave radio is used for long distance transmission.
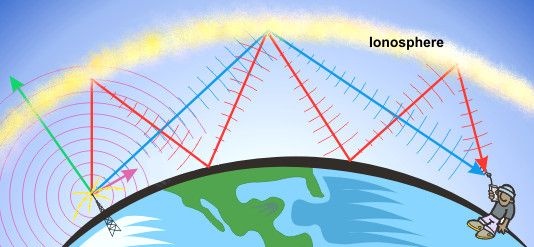
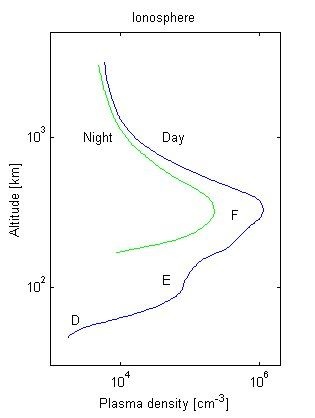
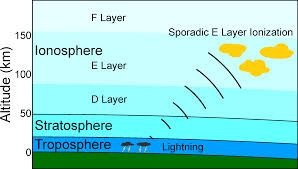
Basically ionosphere is made up of a number of different layers due to ionization at a number of different layers these layers are known as the D, E and F layers. The location of these layers varies by day.
When we study the layer of Earth we will see that the lowest part of the Earth's atmosphere is troposphere and it extends from the surface and up to about 6 miles (10 km). After the troposphere and above 10 km stratosphere start and which is followed by the mesosphere. Stratosphere creates the ozone layer that is having natural work to stop incoming harmful solar radiation.
The lower most region of the ionosphere extending from about 50 km to 90 km is the D region, which principally absorbs radio waves. Above the D layer is the E-region extending form 90 km to 150 km. the peak in the E region during day time is seen near 110 km. above the E region is the F region consisting of two parts the lower F1 region between 150 km and 180 km and the F2 region from 180 km and above. At the day time densities are much larger than the night time densities and at the night, recombination can result in the loss of the D region.
The sun emits radiations which are electromagnetic and due to nuclear fusion process these are harmful for the living objects. When electromagnetic radiation from the sun strips an electron off a neutral constituent in the atmosphere, the resulting electron can spiral along a magnetic field line. Thus Earth's magnetic field plays an important and critical role in propagation.
This is all about the radio and Radio communication. And especially we discuss more emphasizely on the ionosphere and its benefits. It protect the Sun harmful radiation and also helpful in communication up to some extents.