What is 'Rainbow'??
A Rainbow is an 'arc' of colors in the sky which is formed by the shining of Sunlight on water droplets during Rain(s). Here an 'arc' is a constant curved line which is a part of a Circle.
Rainbow is a long and wide band of seven colours (red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo & violet) & it appears in the sky at the end of the rain.. It forms a semi-circle going from one end of the earth to the other.

Image Source:
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/5/5c/Double-alaskan-rainbow.jpg
How 'Rainbow' Is Formed?
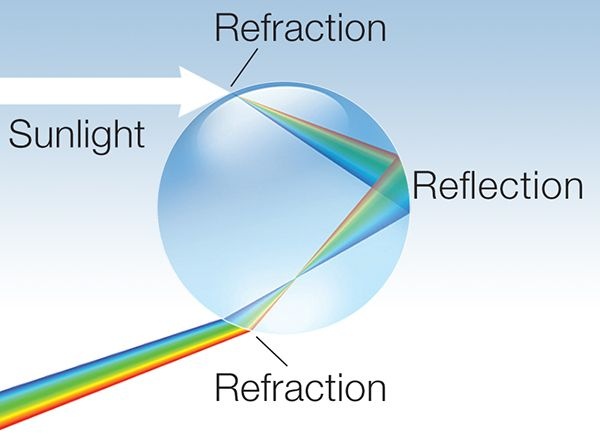
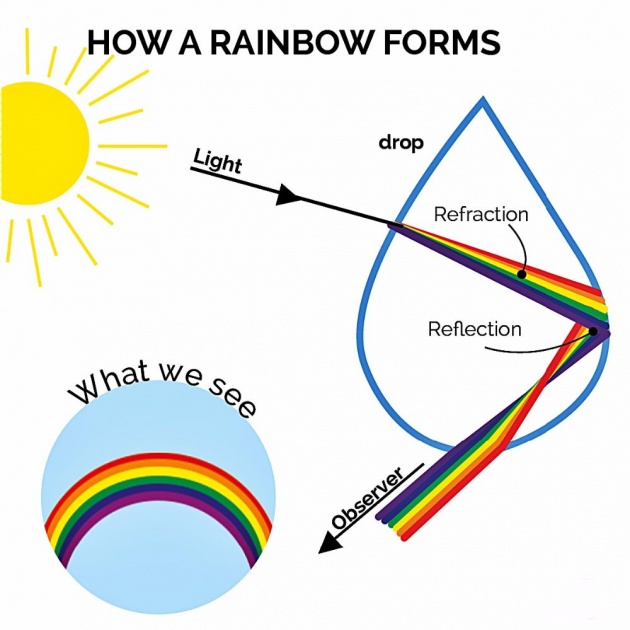
Rainbow is caused by Reflection, Refraction and Dispersion of light in water droplets, splitting that light into a spectrum appears in the sky.
It is because when sunlight strikes the surface of a water droplet (which is a denser medium as compared to air), part of it is refracted into the droplet because when sunlight passes through a lighter medium to a denser medium, it changes its direction (refracted), but due to spherical shape of the droplet, the droplet act as a prism, thus the light reflects in the droplet and then it refracts out in the lighter medium again, resulting in splitting that light into a spectrum & all the seven colours which are present in the white light form a semi-circular rainbow.
<><><><><><><><><><><><><><>
<><><><><><><><><><><><>
Some Important Terms:
1) Reflection:
When light rays strike the surface (boundary) of two medium (such as glass & air), part of light is turned back (reflected) into the same medium. This phenomenon is called reflection of light.
>A highly polished smooth & shiny surface reflects most of the light falling on it. (e.g: a polished mirror), whereas a rough and slightly polished surface reflects a small amount of light.
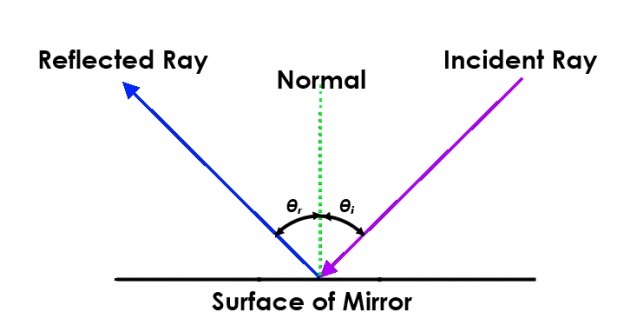
Image Source:
http://www.solving-math-problems.com/images/angle-of-reflection-01-20121207.png
Terms to Remember;
- Incident Ray: A light ray striking a reflecting surface is termed as Incident Ray.
- Angle of Incidence: The angle which the incident ray makes with the normal at the point of incidence. It is denoted by the letter 'i'
- Reflected Ray: The light ray that is obtained after reflecting from the surface in the same medium.
- Angle of Reflection: The angle which the reflected ray makes with the normal at the point of incidence.It is denoted by the letter 'r'.
- Normal: The perpendicular that is drawn to the surface at the point of incidence.
- Point of Incidence: The point at which the incident ray strikes the reflecting surface.
- Plane of Incidence: The plane containing the incident ray and the normal.
- Plane of Reflection: The plane containing the reflected ray and the normal.
<><><><><><><><><>
Laws of Reflection:
i. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection;
angle(i) = angle(r)
ii. The incident ray, the normal, and the reflected ray, all lie in the same plane.
<><><><><><><><><>
Types of Reflection:
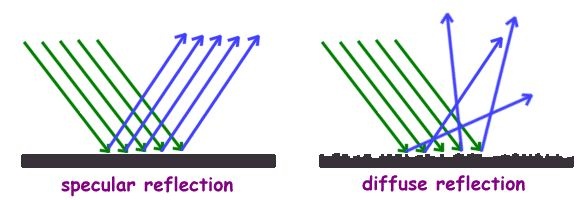
(i) Regular Reflection: It occurs when a beam of light falls on a smooth, shiny & polished surface such as a plane mirror or a smooth & shiny metallic surface. It is also called as Specular Reflection.
(ii) Irregular Reflection: It occurs when a beam of light falls on a rough & dull surface such as wall of a room or a polished piece of wood. It is also termed as Diffuse Reflection.
<><><><><><><><><>
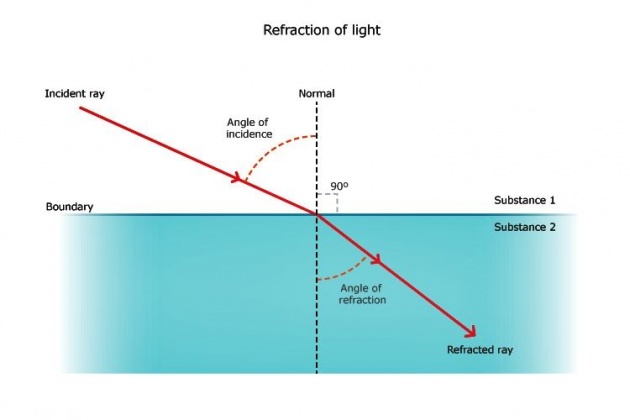
2) Refraction:
Refraction is simply the bending of light as it passes from one transparent medium to another.
*When light rays pass from a lighter medium to a denser one, they bend towards the normal in the denser medium.
*When light rays pass from a denser medium to a lighter one, they bend away from the normal in the lighter medium.
<><><><><><><><><><>
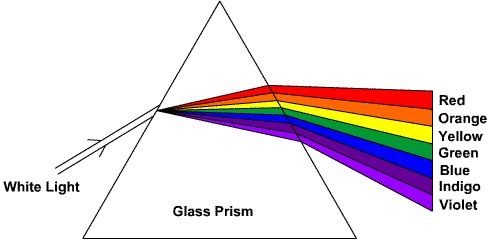
3) Dispersion:
The splitting of white light into different color components (spectrum) is known as Dispersion of light.
White light or visible light consists of the colors red, orange, violet, green, indigo, blue and yellow. This phenomenon can occur when white light travels through a glass prism in which light is refracted at different angles, causing the separation of this light into different colors. Each of these colors has a different wavelength.
<><><><><><><><><><><><>
Rainbow (Cont.)
The Sun is nature’s primary source of light creating rainbow & you cannot have a rainbow without some source of light. But also, it is possible to create an artificial rainbow utilizing artificial light.
People believe that if a rainbow appears after the rain, it is an indication that there will be no more rains. In Hindi, rainbow is called 'Indra Dhanush' which means the Bow of Lord Indra. According to Hindu mythology Lord Indra is the god of rain. [1]
Rainbow(s) can be multiple, twinned, full-circle, supernumerary or monochrome rainbows, depending on the climatic and weather condition(s).
Vision:
The rainbow effect can be seen when:
- There are water drops in the air; and
- the sun is giving light at the back of the observer at a low distance up or angle.
The rainbow displays with the deepest effect in our minds take place when:
- Half of the sky is still dark with draining clouds;
- and the observer is at a place with clear sky above.
Another common place to see the rainbow effect is near waterfalls. Parts of rainbows can be seen some of the time:
- At the edges of clouds lit from the back; or
- as upright bands of spectrum in far away rain even if it does not fall on the earth. [2]
An unnatural rainbow effect can also be made by putting drops of water into the air on a sunny day.

<><><><><><><><><><><><><><><>
Rainbows are not limited to the dispersion of light by raindrops.
- The splashing of water at the base of a waterfall caused a mist of water in the air that often results in the formation of rainbows.
- A backyard water sprinkler is another common source of a rainbow.
- Bright sunlight, suspended droplets of water and the proper angle of sighting are the three necessary components for viewing one of nature's most splendid masterpieces. [3]
Well the rainbow looks miraculously beautiful. Its sight is very soothing to the eye. Small children get very excited when they see a rainbow.
References:
[1] www.preservearticles.com/2011082511731/short-paragraph-on-the-rainbow.html
[2] simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rainbow
[3] www.physicsclassroom.com/class/refrn/Lesson-4/Rainbow-Formation
-Images Source(s): Google Images



