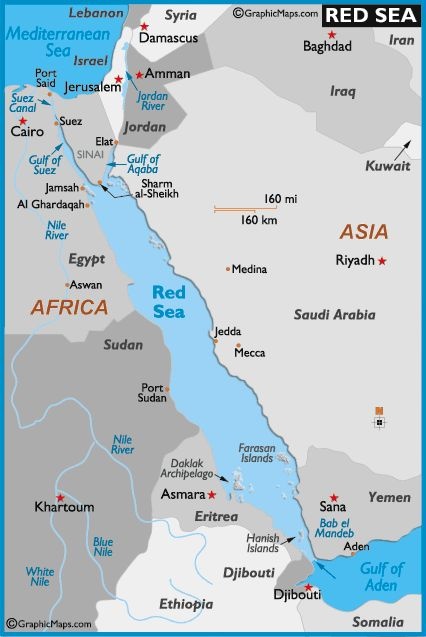
The Red Sea is an extension of the Indian Ocean, located between Africa and Asia, the entrance to the sea in the south is through the Gulf of Aden and the somewhat narrow Bab el Mandeb and in the north the sea is accessed from Middle Eastern countries via the Gulf of Aqaba. The Mediterranean Sea provides a conduit south through the Suez Canal and Gulf of Suez.
This salty sea is just over 300 km across at its widest point, and about 1,900 km in length. There's a measured maximum depth of 2,500 m, and an estimated average depth of 500 m. Much of the immediate shoreline is quite shallow. With hot sunny days, and the lack of any significant rainfall, desert dust storms are known to sweep across the sea. High heat combined with the lack of precipitation facilitates high levels of evaporation - thus the sea's high salinity. Regardless, the consistent sunshine, as well as white sand beaches, pristine coral reefs and a scattering of shipwrecks are major attractions for scuba divers and sun worshipers. Resorts like Sharm al-Sheikh and others in Egypt's "Red Sea Riviera" along the Gulf of Aqaba and Gulf of Suez are fast becoming major tourist destinations.
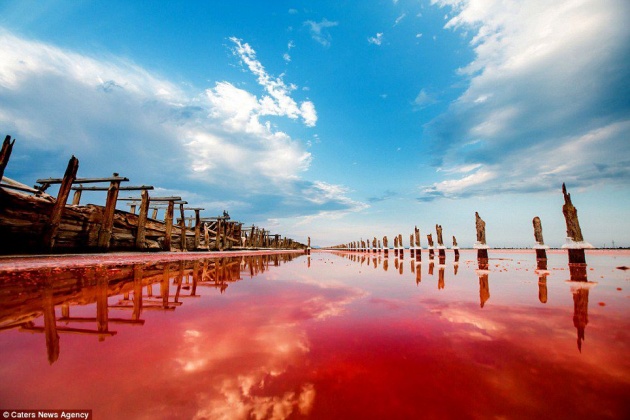
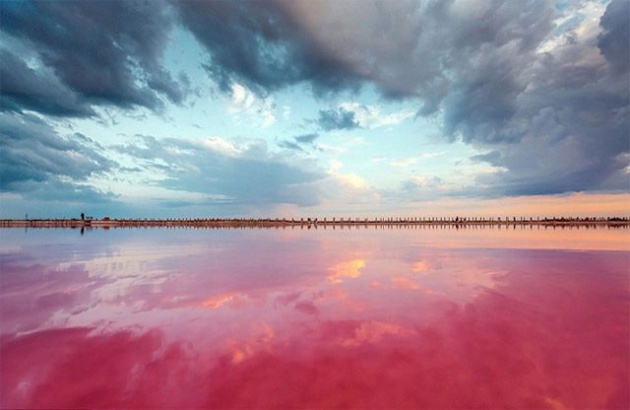
The Red Sea lies between arid land, desert and semi-desert. The main reasons for the better development of reef systems along the Red Sea is because of its greater depths and an efficient water circulation pattern, The Red Sea water mass exchanges its water with the Arabian Sea, Indian Ocean via the Gulf of Aden. These physical factors reduce the effect of high salinity caused by evaporation water in the north and relatively hot water in the south. The climate of the Red Sea is the result of two distinct monsoon seasons; a northeasterly monsoon and a southwesterly monsoon. Monsoon winds occur because of the differential heating between the land surface and sea. Very high surface temperatures coupled with high salinities makes this one of the warmest and saltiest bodies of seawater in the world.
The rain is mostly in the form of showers of short spells, often associated with thunderstorms and occasionally with dust storms. The scarcity of rainfall and no major source of fresh water to the Red Sea result in the excess evaporation as high as 205 cm per year and high salinity with minimal seasonal variation. A recent underwater expedition to the Red Sea offshore from Sudan and Eritrea found surface water temperatures 28 °C in winter and up to 34 °C in the summer, but despite that extreme heat the coral was healthy with much fish life with very little sign of coral bleaching.
Salinity ranges from between ~36% in the southern part because of the effect of the Gulf of Aden water and reaches 41% in the northern part, owing mainly to the Gulf of Suez water and the high evaporation. The salinity of the Red Sea is greater than the world average, approximately 4%, being the average salinity of the red sea 40%.
This is due to several factors:
- High rate of evaporation and very little precipitation.
- Lack of significant rivers or streams draining into the sea.
- Limited connection with the Indian Ocean, which has lower water salinity.
The Red Sea is a rich and diverse ecosystem. More than 1200 species of fish have been recorded in the Red Sea, and around 10% of these are found nowhere else. This also includes 42 species of deepwater fish, Red Sea coral and marine fish.
The rich diversity is in part due to the 2,000 km of coral reef extending along its coastline; these fringing reefs are 5000–7000 years old and are largely formed of stony acropora and porites corals. The reefs form platforms and sometimes lagoons along the coast and occasional other features such as cylinders (such as the Blue Hole (Red Sea) at Dahab). These coastal reefs are also visited by pelagic species of red sea fish, including some of the 44 species of shark. The Red Sea also contains many offshore reefs including several true atolls. Many of the unusual offshore reef formations defy classic coral reef classification schemes, and are generally attributed to the high levels of tectonic activity that characterize the area.




Information source: Wikipedia.



