Defnation
the conductor which show zero conductivity at very low temperature called as superconductor.
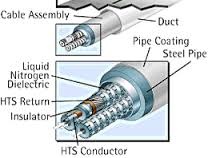

There are major laws to understand how a superconductor works are given below
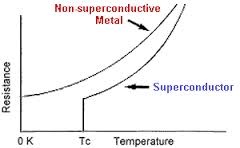
Charge mobility in superconductor
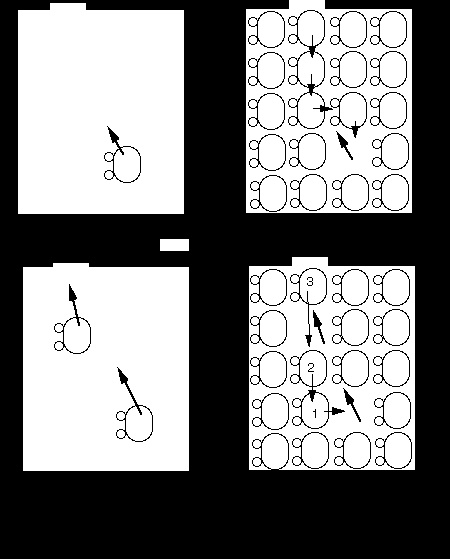
This theory shows that an atom at right temperature can attrackt instead of repel each other are superconductor. This phenomena was presented in a theory named as BCS theory was presented by (Jhon Barden, Leon Cooper, Robert Schrieffer).
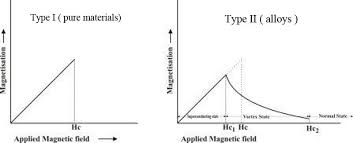
Types of superconductors
There are two types of superconductors are commonly being used now a days in modren power electronics
Type I superconductors
- Pure metals (30 discovered).
- Zero resistivity at very low temp.
- Show missner effect.
- Superconductivity exists only below critical tem and critical megnatic field.
- They are described by bcs theory
.
Type II superconductors
- Mostly allowys e.g (lead-bismith alloy)
- Have much higher critical field.
- Could carry much hiegher current densities while remaing in superconducting state.
Uses of superconductors
- Maglev (megnatic levitation) bullet trains

- SQUIDS (superconducting quantom interferance devices). Are can detect even weakest megnatic field used in mine detection equiqments.
- Used in generators and motors (1/10 th weight reduction)
- Used in transmission lines for 10—15 % weight reduction and to save the energy.
- “E-bombs” device that can make use of strong superconductor pulse the disable enemy’s electronics equipments.



