بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
Today I write a blog and this blog about the Solubility .in this blog I write what is solubility and what is it factor who’s affected on the solubility. So first of all I write About the Solubility
Solubility:
The amount of solute in necessary to Saturate 100 g of the solvent at a particular temperature is known as the Solubility. Different substances have different solubility’s in the same amount of solvent at a specific temperature

Example of Solubility:
Sodium nitrate is more soluble as compare to the silver chloride in the water. .Generally we see that the solubility of a solute is taken to be the quantity required to make a sutured solution in a given quantity of the solvent.
Factors affecting on Solubility:
Following are the factors that affect the solubility of a solute
1) Temperature
2) Pressure
3) Nature of solute

4) Nature of solvent
Temperature:
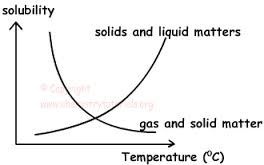
It is often observed that of many solutes in solution generally increase with the increase temperature. Such solute absorbs heat on dissolution (endothermic process) the solubility of some decrease also with the increase in temperature. Such solute generated heat when dissolved in water. Gases are more soluble in cold solvent as compared to hot solvent when a solution containing a gas in a liquid is heated, gas is evolved.
Example of Temperature:
The solubility of potassium nitrate increase with the increase in temperature
Calcium oxide is less soluble in hot water as compared to cold water because it liberates heat on dissolution (exothermic process)
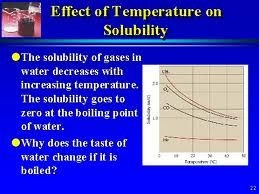
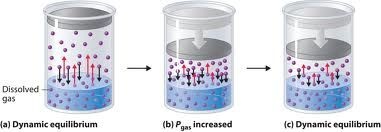
Pressure:
Since solid and liquid are incompressible therefore the solubility’s of solid and liquid are not affected by the changing of the pressure. Solubility of gases increase with the increase with increase in pressure.
Example of pressure:
Carbon dioxide is filled in soda water bottles under the pressure .when a bottle of soda water is opened carbon dioxide comes out with effervescence (bubbles) because pressure in the bottle is released resulting in decrease in the solubility of the gas
Nature of solvent:
When the molecules of solute are similar in structure and properties to the molecules of the solvent, the solubility is greater “Like dissolve like"
Example of solvent:
Sodium chloride is an ionic compound it has greater solubility in a polar solvent but low solubility in a non – polar like benzene
Nature of solute:
It also affects solubility if a solute is changed in the same solvent, the solubility changes.
Example of solute:
Sodium chloride has high solubility in water and sugar has comparatively low solubility