GEOLOGICAL STRUCTURAL FEATURES
OR STRUCTURAL FEATURES OF ROCKS
Simply know as “Structural Features” or “Rock Structures”
- Rocks on and within the earth are subjected to a number of internal and external forces acting in various directions, intensities and sets
- Size, shape and arrangement of component units of rocks are the result of interaction of these forces
- Structural Geology deals with the morphology, classification, mechanism and causes of development of these rock structures
Primary and Secondary Structural Features of the rocks:
(i) Primary Structural Features: These are the Structural Features which are developed in the body of a rock during its formation stage. Crystalline Structure is Primary Structural Feature of Igneous Rocks; Stratification and Lamination are the Primary Structural Features of Sedimentary Rocks, and Foliation is Primary Structural Features of Metamorphic Rocks
GEOLOGICAL STRUCTURAL FEATURES
OR STRUCTURAL FEATURES OF ROCKS
(ii) Secondary Structural Features: These are the Structural Features which are imposed upon or experienced by the rocks after their original formation has been completed. Diastrophism is also a Secondary Structural Feature
Diastrophism: A process of earth’s deformation caused by the large-scale movement of the earth crust which causes the formation of major features of the earth surface including continents, mountains, ocean beds, folds and faults

Diastrophism or large-scale earth movement includes two types of movements: (a) Epeirogenic Movement: It is vertical movement or movement in the vertical plane; it doesn’t cause much deformation
(b) Orogenic Movement: It is horizontal movement; it causes considerable deformation and displacement. It results in folding, breaking and crushing of rock mass; it chiefly includes the mountain building activity – Orogeny

GEOLOGICAL STRUCTURAL FEATURES
OR STRUCTURAL FEATURES OF ROCKS
Secondary Structural Features are more important in Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rocks as compared to those in Igneous Rocks because Igneous Rocks undergo least deformation after their original formation as compared to the other two types of rocks

Important Structural Features (called as “Structural Defects” by Terzaghi – Karl Von Terzaghi: An Austrian Civil Engineer and Engineering Geologist known as Pioneer of Engineering Geology and as Father of Soil Mechanics; had been working between 1910 - 1950)
(i) Primary or Major Structural Features: Fold, Fault, Joint, Fracture and Cleavage
(ii) Secondary or Minor Structural Features: Unconformity, Overlap and Outcrop

GEOLOGICAL STRUCTURAL FEATURES
OR STRUCTURAL FEATURES OF ROCKS
(i) Primary or Major Structural Features:
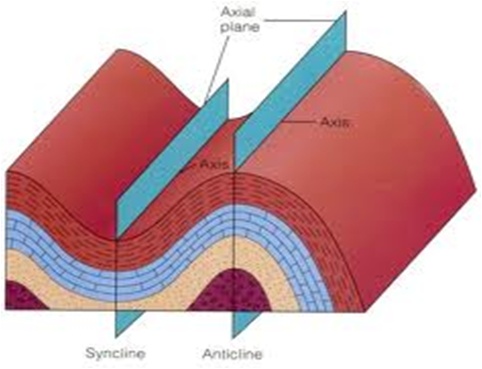
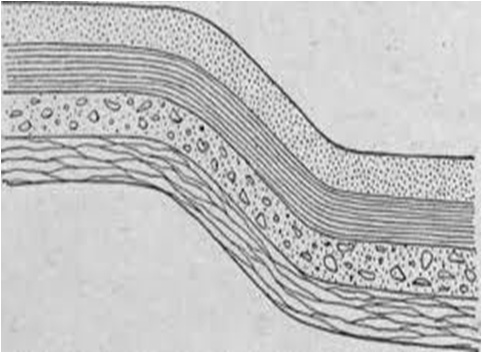
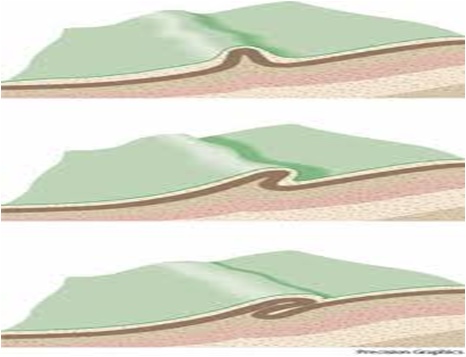
(1) FOLD: It is defined as undulation or bend across the stratification of rock body developed by the stresses caused due to Lateral Compression
Up or crest in the undulation is called Anticline (also known as Antiform) and vice-versa for Syncline (also known as Synform)
Monocline is a partial bend or a slope equal to about half of an anticline or quarter of a waveform

Isoclines are the folds whose limbs (Limb: arm of a fold) are (more or less) parallel
Characteristics of Folds: Folds are important in the quarrying (as well as in mining) especially in sedimentary rocks – floors, benches and faces are developed according to the slope of the slant of the folding. In dams and tunnels, water leakage usually takes place along the slant of fold if they slope towards downstream