When a temperature of a material is reduced much below the room temperature, the thermal vibration of the lattice ions decreases.This results in the decrease of the resistivity of the material. But the resistivity of the class of materials(metals, allovs and ceramics),however,drop suddenly at the certain critical temperature Tc to an immeasurable small value (almost zero).The drop in the resistance occur over an exceedingly small temperature range, as i show in this figure.
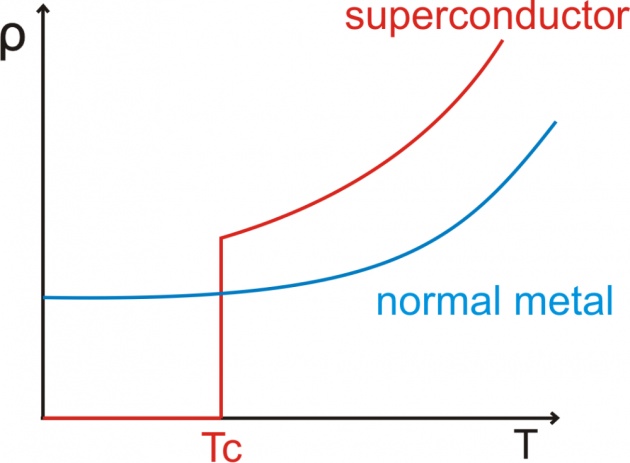
Materials whose resistance vanishes at low temperature are called superconductors and the phenomenon is called superconductivity.Before 1986 the highest Tc attained was 7.17 below which some metals were superconductors.In 1986 it was discovered that some ceramics exhibit superconductivity at T.=30 K. Recently, a complex crystalline structure known as Yttrium barium copper oxide(YBa2Cu3O7)
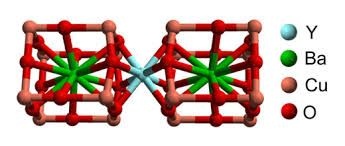
has been reported to become superconductor at 163 K or (-110 C) by Prof. Yao Lian's at Cambridge University.Efforts are going on to find materials that could show superconductivity even at room temperature.The benefit of superconductivity is its ability to supply electrical energy without any loss.This would save a handsome amount of energy in future.Superconductors have many technological applications such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI),magnetic levitation trains, powerful but small magnetic motors and faster computer chips.




