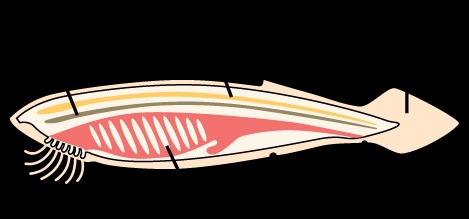
1. Notochod: It is a flexible rod like structure situated along the mid dorsal line between the gut and nerve cord. It is the first part of the endoskeleton to appear in the embryo. It is derived from the embryonic chorda mesoderm. It is made up of a core of ‘vacuolated cells’ surrounded by an inner think fibrous and an outer thin elastic connective tissue sheaths.
2. Dorsal Tubular Nerve Cord: A single, hollow tubular and fluid filled nerve cord is situated above the notochord and below the dorsal body wall. It is non-ganglionated, unlike that of the non-chhordates. It is produced in the embryonic stage by the ‘sinking in’ of the median dorsal strip of ectoderm above the notochord. In the higher chordates, it gets enlarged to form a distinct brain at the anterior end and the rest of it.
3. Pharyngeal slits or clefts: Pharyngeal slits are a series of lateral perforations in the wall of the pharynx through which water flows out from the pharyngeal cavity. They are ecto-endodermal in origin. They are persistent throughout the life in the protochordates, fishes and some amphibians. They are persistent throughout the life in the protochordates, fishes and some amohibians.
4. Post-Anal Tail: Chordates have a tail extending posterior to the anus. It is lost in many species during the late embryonic development. It contains skeletal elements and muscles.



