Hello fellow, as I promised you all to write about our wonderful body and human health, here this is my second blog about “The Human’s Wonderful Body”.
The Human Skeletal and the Muscular System
The Human Skeleton:
The human skeleton is the framework of bones in our body. This framework of bones encloses the internal organs giving support, strength, and shape to the body. An adult body has 206 bones of different sizes and shapes. The bones have blood vessels and nerves.
What is The Human Skeleton?
Video Credit: Human Anatomyx Via YouTube
The human skeleton consists of the skull, the backbone, the ribs and the breastbone (Sternum). There are two pairs of limbs, which are attached to two pairs of girdles (belt).

Photo Credit: The K8 School
The Skull:
The skull is made up of 8 flat bones, interlocked together. They enclose the delicate brain inside it. Fourteen bones make up the facial region. Only the lower jaw is moveable which is enables us to eat and talk.
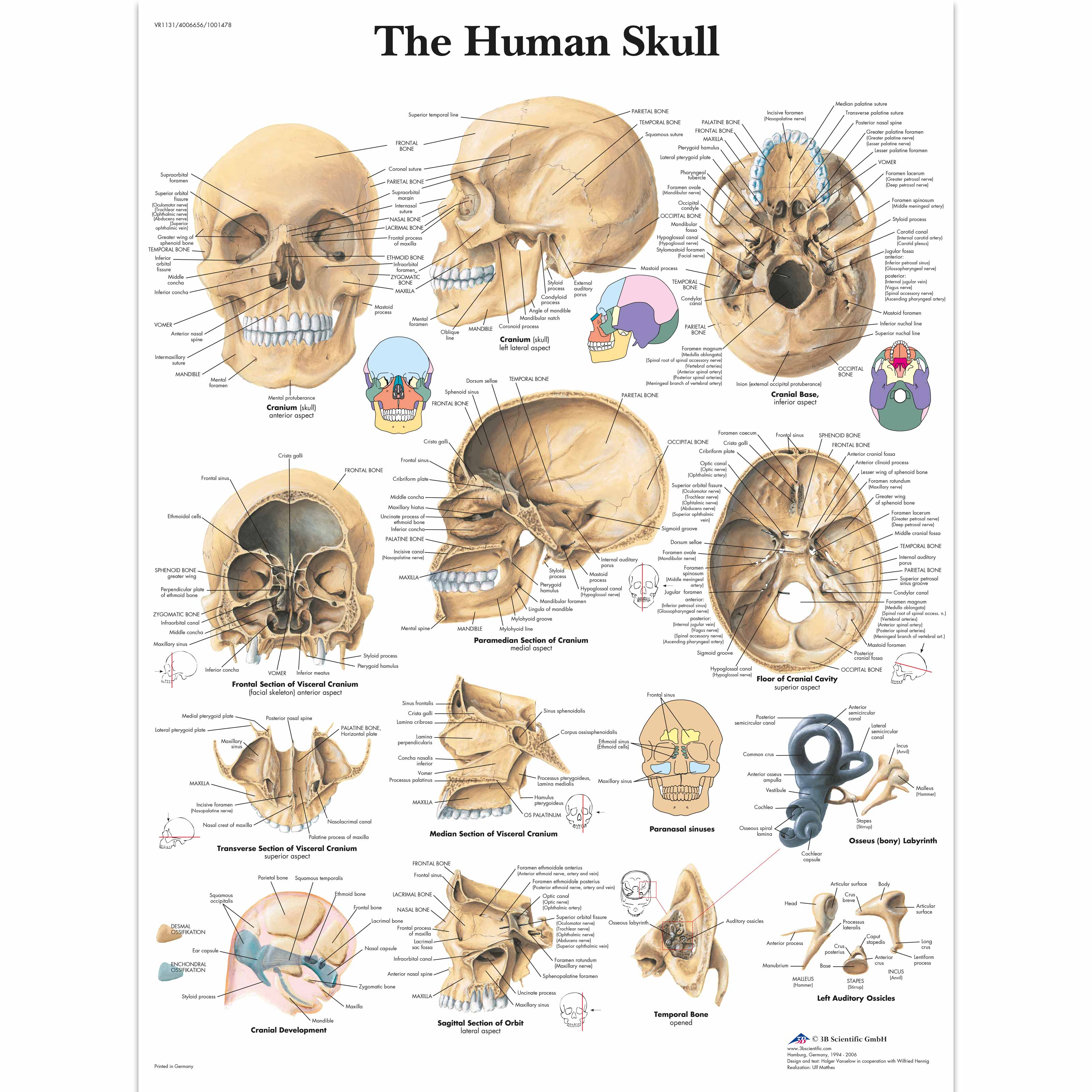
Photo Credit: 3B Scientific
The Backbone and The Spine (Vertebral Column):
The skull is attached to the backbone, which forms the main axis of the skeleton. It is made up of 33 small bones, forming the strong column that protects the delicate spinal cord.

Photo Credit: by Dr. Chirs via Health Hype.com
The Rib Cage:
There are twelve pairs of ribs forming a cage, enclosing the heart and the lungs. The ribs are delicate, curved bones which are joined to the backbone and the breast bone (Sternum). The last two pairs, called floating ribs are joined only to the backbone.

Photo Credit: Anatomy Organ
The Limbs:
The forelimbs or the arms are joined to the spine with the help of the shoulder girdles, consisting of a pair of shoulder blades and a pair of collarbones.
The powerful thigh bone or Femur, "the longest bone in our body", bears the weight of the whole body. The femur fits into the hip girdle with a ball-and-socket joint and is connected to the lower leg with the knee joint. The long bones of the skeleton are hollow and are filled with a soft, fatty substance called “Bone Marrow”.

Photo Credit: The Pirate Surgeon’s Journals
Functions of the skeleton:
The skeleton gives shape and strength to our body. They also protect our internal organs. The skull covers the delicate brain; the eyeballs rest inside the bony eye sockets, the backbone protects the spinal cord and the rib cage shields the lungs and the heart. The urinary bladder lies inside the hip girdles. The muscles attached to the bones make the movement of the body possible. White blood cells which fight infection and red blood cells are produced by the bone marrow in hollow bones. Calcium and phosphorus are stored in the bones. They make the bones firm and strong.

Photo Credit: Mr. Lloyd Scientists
Joints:

Photo Credit: Louisan.info
A joint is the meeting point of two bones. Joints are held together by strong tissues called LIGAMENTS. There are several joints in our body. Movement is possible at all the different joints except the skull. The bones of the skull are interlocked making the joints immovable. There are three kinds of joints;
Fixed joints or Synarthrosis:
In this kind of joints, the bones cannot move. Joints between the bones of our skull are fixed joints.
Slightly moveable joints or Amphiarthrosis:
Bones can move a little in this kind of joints. For example, joints between our vertebras.
Freely moveable joints or Synovial joint:
The bone can move freely in this kind of joint. There are freely moveable joints at our knees and elbows.
"Types of the Joints in Human Skeleton"
Video Credit: Iken Edu Via YouTube
The bones at the joints move smoothly because of a fluid which acts like a lubricate. There are four types of “moveable joints” in our body.
i) The hinge joints:
A hinge joint is like a hinge in a door. It can move the bones only in one direction. It is found on the elbows, knees, fingers, toes, etc.
ii) The ball-and-socket joints:
A ball-and-socket joint allows the maximum movement, as displayed by ballet-dancers. One bone that ends in a ball fits into the socket of the other. It is found in the hip and shoulder joints.
iii) The pivot joints:
A pivot joint is found between the skull and the first two vertebrae of the spine. The uppermost vertebrae in the neck are called the “Atlas”, named after the Greek god who carries the globe on his shoulder. With the help of the pivot joint, we can move our head sideways, upward and downward.
iv) The Gliding or Plane Joint:
This kind of joint allows movement at the wrist and ankle and also between any two vertebrae of the spine. It allows our back to bend, twist and turn at each joint.
Imagine your backbone made up of just one long bone! Would it make you look stiff as a scarecrow?

Photo Credit: Ency123
The Muscles and the movement:
The muscles in the body tighten and produce movement. There are about 650 muscles in the body, and each one causes a particular movement. Muscles bend our arms and knees, push food in the digestive canal, allow us to inhale air into our lungs, chew our food, and make our heart beat. Muscles are attached to the bones by strong fibre called “Tendons”. These fibres become stronger with regular exercise.
Types of Muscles:
There are three types of muscles, Voluntary or Skeletal Muscles, Involuntary or Smooth Muscle Tissues Muscles, Cardiac Muscles.
i) Voluntary or Skeletal Muscles:
Some Muscles in our body are under our control, so we call them “Voluntary or Skeletal Muscles”, like the muscles attached to our bones. When we decide to move, they pull on our bones, and our joints are bent. These muscles work quickly and powerfully, but they soon get tired.
ii) Involuntary Muscles or Smooth Muscle Tissues:
Other muscles, which are not under our control, are called “Involuntary Muscles or Smooth Muscle Tissues”. They keep working on their own. They control actions like the movement of food in the alimentary canal, the flow of blood and the movement of the eye muscles. Involuntary muscles work slowly and do not get tired.
iii) Cardiac Muscles:
The third kind of muscles is found in the heart, which is involuntary in function but structured like voluntary muscles. These muscles are called “Cardiac Muscles”. The cardiac muscles work without getting tired all through our lives. They pump blood all around our body.

Photo Credit: Nutri NZ
Do you Know Guys! How do Muscles Works? Let me tell you.
Muscles produce movement in the body, by pulling on the bones. When muscle contracts, the bones come closer to each other. When the knee bends, one muscle contracts and gets shorter, whereas the other one relaxes. When the leg is stretched, the reverse happens. Well developed muscles give a graceful appearance to the body. One must maintain good posture while sitting or standing to keep the muscles in good shape. A poor posture looks awkward and causes fatigue.

Photo Credit: By Wendy Whyte Via Slide Share in
So here it is guys, I am planning to write about our nervous system or Excretory System, let see, which topic I will choose.
I will write the post on the topic, which I can write something best easily and in simple words to make it easy for understanding. Suggest me the topic guys in comments, Vote for “The Human Nervous System” or “The Human Excretory System”, but before these blog posts, I will write a post about Sir Micky’s topic of double reward.
Till then “TATA Bye Bye.”
Regards:
© Copy Right-InX_GL All right reserved 2017
Take part in the Querlo Chat Survey given below about Diet and Healthy life style.
Querlo Survey Credit: Find a Link in Fredo898's blogs posts via bitlanders.com



