I remember, as a boy of 17 years of age, this was a fascinating thing for me: how we human beings breathe out carbon dioxide into the air, the leaves of plants fill this carbon dioxide up, and the plant gives off oxygen, which we can breathe in and keep our life going.
Plants are the most important living things in the world. Without them, no animals, including human beings could exist. This is because green plants are the original source of all food.
We eat meat. The cattle from which we get meat could not grow without first eating food themselves-in this case grass. Our bread is made from flour. Flour is made from wheat which is a plant. All our food-and the food of all other animals-can be traced back to plants in this way.
Plants also supply is with the wood to build our houses and furniture, and the paper for our books and newspapers. Many of our clothes are made from plants fibers. Plants provide us with drugs, medicines, and perfumes. They also fill our houses and gardens with beauty and scents.
Plants are the most successful of all living creatures. Many of them live longer and grow larger than any animal. Some of California's famous redwood trees grow 350 feet (107 meters) high, and are more than 3,000 years old.
PLANTS OR ANIMALS
Botanists, scientists who specializes in the study of plants, have named more than 350,000 kinds of plants. But often they find it difficult to decide whether a living thing is a plant or animal. Here are some of the guide-lines that help them to determine which is which.
Most plants seemed to be fixed; most animals seem to be able to move about. Most animals take food in through their mouths, and discharge waste products after the food has been digested; most plants are unable to do this. Most plants have chlorophyll. This is a green coloring substance that enables them to use the sun's energy to make food. Most animals do not have chlorophyll. The cell walls of most plants are made up mainly of cellulose. This is a chemical substance that forms the woody parts of plants. Animals do not have cellulose in their bodies.
How can the Chlorophyll Help our Body?
The video is taken from Youtube. No part of this video may be reproduce without special credits from the video owner Beautymorphosis.
References:
- https://www.biography.com/people/groups/scientists-botanists
- https://slideplayer.com/slide/7096153/
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322361.php
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cellulose
MAKING AND STORING FOOD
One of the main differences between the plants and animals is the way plants make their own food.Green plants make their own food by taking in water from the soil through their roots. They also take in carbon dioxide from the air through their leaves. The water and carbon dioxide combine to make sugar, and the plants give off oxygen. This process is known photosynthesis.
The energy for this process comes from the sunlight. If plants are kept in the dark, photosynthesis stops. (The word 'photosynthesis' comes from the Greek words, meaning 'putting together with light'.)Once a plant has made sugar it can form starch and all other substances it needs for life.
Food is stored in the roots of a plant. The roots also anchor the plant to the soil.
Discovery
Although some of the steps of photosynthesis are still not completely understood, the overall photosynthetic equation has been known since the 19th century.
Jan van Helmont began the research of the process in the mid-17th century when he carefully measured the mass of the soil used by a plant and the mass of the plant as it grew. After noticing that the soil mass changed very little, he hypothesized that the mass of the growing plant must come from the water, the only substance he added to the potted plant. His hypothesis was partially accurate-much of the gained mass also comes from carbon dioxide as well as water. However, this was a signaling point to the idea that the bulk of a plant's biomass comes from the inputs of photosynthesis, not the soil itself.
Read more in this source and credits: Wikipedia
References:
- https://www.livescience.com/51720-photosynthesis.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Photosynthesis
- https://msu.edu/user/morleyti/sun/Biology/photochem.html
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9781118981771.ch9
KINDS OF PLANTS
The plant kingdom can be divided into to main groups: no-flowering plants and flowering plants. Flowering plants make up the largest and best-known group.
Non-Flowering Plants
Algae are among the most primitive of the non-flowering plants. They form the green slime that can sometimes be seen on ponds. But they also include giant seaweeds of various colors. Microscopic algae form floating masses off vegetation called plankton, which is found in lakes and seas. This is a valuable source of food for almost all fish and other sea animals.
Liverworts are small, flat, green leaf-like plants. They grow in clusters in damp places, such as the banks of streams or in caves open to the light. Liverworts are closely related to mosses.
Mosses, together with liverworts, may have been among the world's first plants. They are tiny green plants which grow close together. They form carpets of vegetation on damp earth, rocks, and trees.

(The image of fern originally owns by the author via bitlanders.com, taken from iphone6plus.)
Ferns generally grow in moist, shady places. There are about 10,000 different kinds. Some are like mosses, while others are as large as trees. Their leaves, usually feather-like are called fronds. This group also includes bracken.
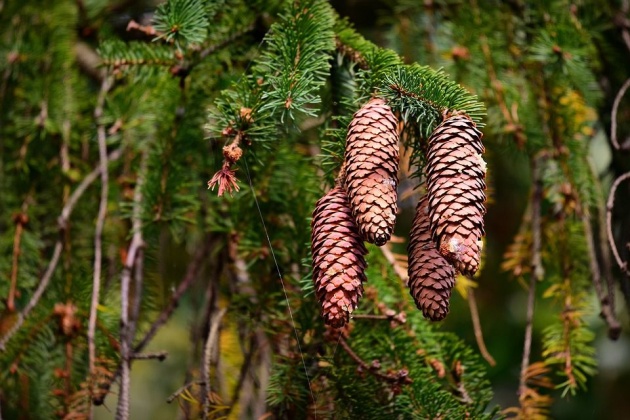
Cone-bearing trees, or conifers, are a large group of trees and shrubs whose flowers have become cones or scales. Most conifers have small, evergreen, needle-shaped leaves. Pines, larches, spruces, cypresses, yews, and cedars belong to this group.
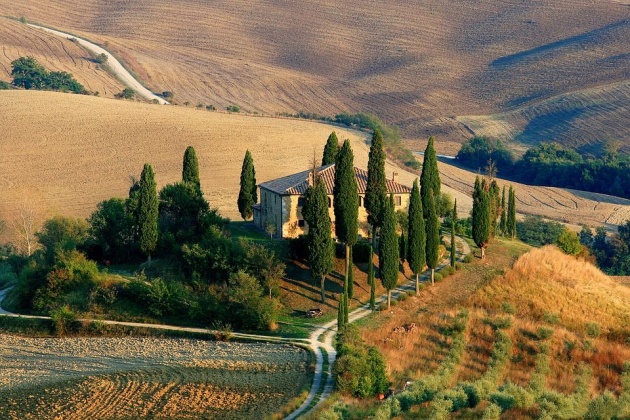

In the picture above is the cypress that belongs to a large group of trees called conifers. (The image is from pixabay. Credits to the owner Kasabubu). In the picture below is the conifer that produces cones and usually have small, needle-like leaves. (The image is from Pixabay. Credits to the owner Mabel Amber).

References:
- https://www.encyclopedia.com/plants-and-animals/microbes-algae-and-fungi/moneran-and-protistan/algae
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microalgae
- https://www.britannica.com/plant/liverwort
- https://basicbiology.net/plants/non-vascular/mosses
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fern
- https://kids.britannica.com/students/assembly/view/171827
PLANT KINGDOM: SOME MAIN DIVISION
1) PRIMITIVE PLANTS
- Chlorophyta- Green Alga
- Schizophyta- Bacterium
- Fungi- Bread mould
2) NON-FLOWERING PLANTS
- Hepaticae- Liverwort
- Lycopodineae- Small clubs moss
- Equisetineae- Horsetail
- Filicineae- Fern
- Gymnospermae- Conifer
4) FLOWERING PLANTS
DICOTYLEDONEAE (DICOTS):
- Birch tree
- Violet
MONOCOTYLEDONAE (MONOCOTS):
- Palm tree
- Lily
Fungi, unlike green plants, do not contain chlorophyll and, as a result, cannot feed themselves. This mean that they are all either saprophytes or parasites. Saprophytes are plants that only feed dead matter. Parasites are plants or animals, that feed off a living source-that is, another plant or animal. Fungi are found all over the world, and include moulds, mildews, yeasts, toadstools and mushrooms.
Reference:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fungus
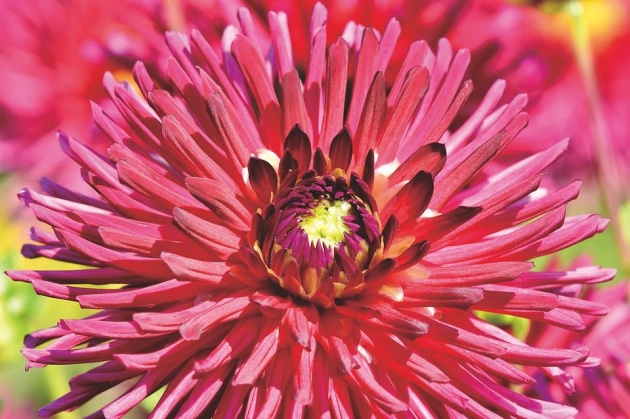

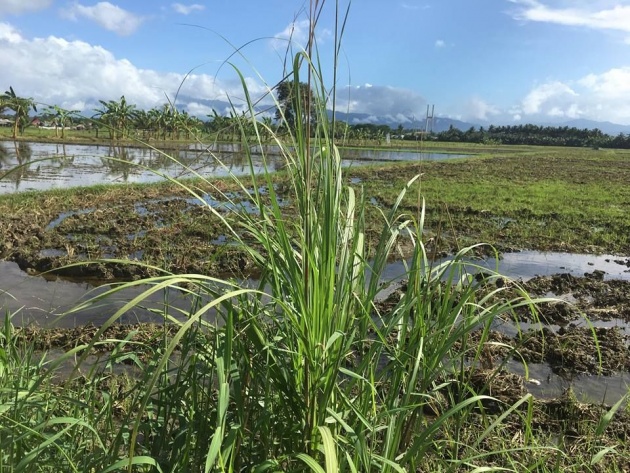
Two types of flowering plants are dicotyledons and monocotyledons. Dahlia (above) is dicotyledon. (The image is from Pixabay. Credits to the owner Capri23auto. The grasses below are monocotyledons.(This image is originally owned by the author via bitlanders.com taken by iphone 6plus).

Flowering Plants
Flowering plants are plants that are mostly familiar to us. They are made of of roots, stems, leaves, flowers or blossoms. The flowers are the reproductive parts of the plants. They sometimes have the strong scent and are often very colorful. There are about 200,000 kinds of flowering plants. They grow everywhere in the world except at the North and South Poles.
Flowering plants are divided into two groups. Monocotyledons grow from a seed without a single seed leaf. Dicotyledons grow from a seed with two leaves. The two groups differ in many important ways.
Monocotyledons usually have narrow leaves with veins that run parallel. The parts of their flower, such as stamens and petals are usually arranged in threes of sixes. There are about 40,000 kinds of monocotyledons. They include bananas, pineapples, grasses, reeds, rushes, cereals, irises, and daffodils.
Dicotyledons usually have broad leaves with a network of veins. The parts of their flowers are usually arranged in fours or fives. Dicotyledons maybe further subdivided into herbaceous plants, shrubs, and deciduous trees.
Herbaceous plants are flowering plants whose shoots, the parts above the ground, live for only a year. Their roots, however, may live underground for year after year in the same place. Daisies, buttercups and dandelions are herbaceous plants.
Shrubs are bushy plants with woody stems which live for a long time. They are smaller than trees and have many branched stems near the ground instead of one central trunk. Blackthorns, hawthorns, boxes and privets are shrubs.
Deciduous trees are those that shed their leaves regularly at the end of the growing season. Oaks, hazels and beeches are deciduous trees.
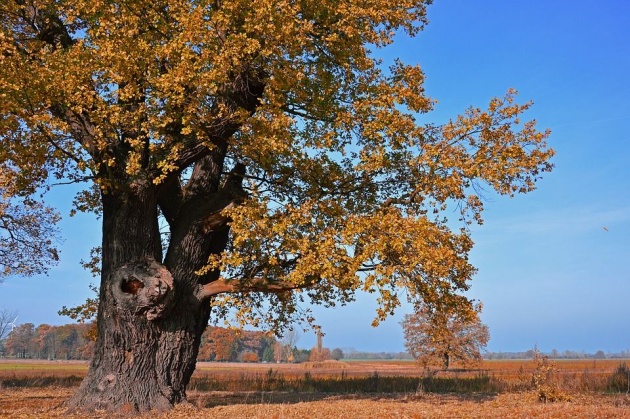

Deciduous tree (Above) and the birch tree (below), are among the great variety of plants which can be seen at Kew Gardens (below birch tree) near London.(The image above is from Pixabay. Image credits to the owner Peggychoucair. The image of the birch tree below is from Pixabay. Credits to the owner Free-photos).
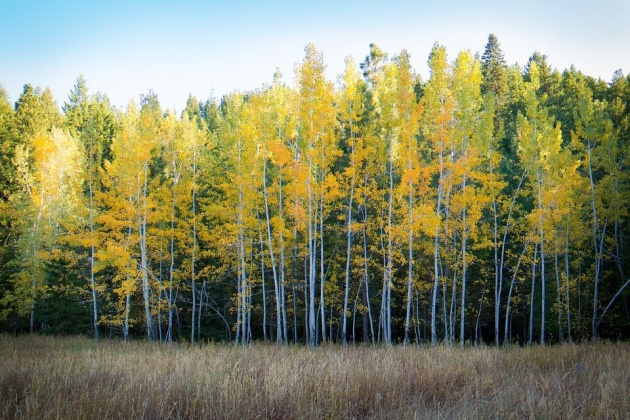

The Great Variety of Deciduous trees and Birch Trees at the Kew Garden near London
The video is taken from Youtube. No part of this video may be reproduce without special credits from Mel and Jona Travel.
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flowering_plant
- https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Herbaceous_plant
- https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-are-deciduous-trees-types-definition-examples.html
The blackberry (above) is a perennial, a plant that lives for several years. (The image is from Pixabay. Image credits to the owner Makamuki0). The zinnia (below) is an annual, completing its life-cycle in a year. (The images of zinnia below is originally owned by the author via bitlanders.com).
Length of Life
Gardeners often prefer to classify, or arrange, cultivated plants (plants that do not grow wild) according to their life-cycles. They recognize three main groups: annuals, biennials and perennials.
Annuals normally complete their life-cycle within a year. In that time, they grow from seeds mature into fully grown flowering plants, produce new seeds and die. But some gardeners also use the terms 'annual' to describe any plant that blooms within a year of being sown from seed, regardless of how long it lives. Cornflowers, marigolds, and zinnias are common annuals.
Biennials are plants that take two years to complete their life-cycle. Most of them develop into sturdy plants during their first year, and only bloom in the second year. Carrots, radishes, foxgloves and hollyhocks are all biennials.
Perennials are plants that survive for several years. They do this by putting out new shoots each year, or by having woody stems. Some woody-stemmed plants, such as roses, may live indefinitely. Other popular perennials are carnations, prime-roses, and violets.
References:
- https://www.almanac.com/plant/marigolds
- https://www.almanac.com/plant/zinnias
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Annual_plant
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biennial_plant
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Perennial_plant
PLANTS AND MAN
With new advances in science, man has been able to improve the plants that are useful to him. He has also, to a great extent, been able to destroy those that are useless or harmful.
By careful cross-breeding, he has improved the food quality of many nutritious plants. He has developed new types of cereals, fruits, and vegetables that will grow well in unfavorable conditions. And he has succeeded in producing varieties of useful plants that can stand up against disease and insect pests.
Unfortunately, in this enthusiasm to protect certain cultivated plants, man has sometimes used chemical sprays and washes that have poisoned other forms of life. As a result, many birds, bees, and other animals and wild plants have been completely destroyed in certain areas. Such action can only disturb the balance of nature, and man may yet find that he has created more problems than he has solved.
The list credits, by article, other source of illustrations, used by the author of "The Plant World." Credit goes to Pixabay.
All rights reserved. No part of this Article
may be reproduced without the special credit
in writing from the publishers in
Wikipedia.org, almanac.com, study.com, britannica.com, basicbiology.net, kidsbritannica.com, livescience.com, msu.edu, and onlinelibrary.wiley.