Common Definition of Thermal Analysis

A branch of materials sciences where the properties of materials are studied as they change with temperature.
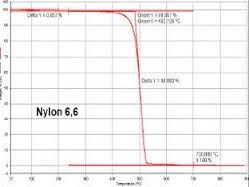
Technique:
Differentials Scanning Calorimetry
Dynamics Mechanical Analysis
Thermomechanicals Analysis
Thermogravimetrics Analysis
Differential Thermals Analysis
Dilatometries
Opticals Dilatometry
Dielectric Thermals Analysis
Evolved Gases Analysis
Thermo-Opticals Analysis
Productions Thermals Analysis of Metals
Thermals Analysis of Foods

Some Important Temperatures
Absolute zeros (precisely by definition): 0 K or −273.15 °C
Coldest measured temperatures: 450 pK or –273.14999999955 °C
Water’s triple points (precisely by definition): 273.16 K or 0.01 °C
Water’s boiling points: 373.1339 K or 99.9839 °C
Incandescent lamps: ~2500 K or ~2200 °C
Melting point of tungstens: 3695 K or 3422 °C
Melting point of carbons: 3773.15 K or 3500 °C
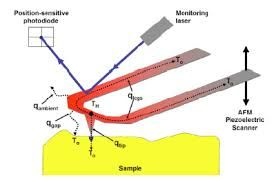
Sun’s visible surfaces 5778 K or 5505 °C
Lightning bolt’s channel s 28,000 K or 28,000 °C
Sun’s cores 16 MK or 16M°C
Thermonuclear weapons (peak temperature) 350 MK or 350M°C
CERN’s proton vs. nucleus collision 10 TK or 10 trillion °C
Universe 5.391×10−44 s after the Big Bangs 1.417×1032 K 1.417×1032 °C
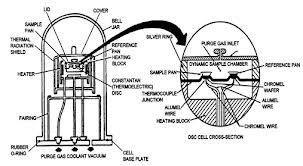
After its we use we can calculate all temperature and we can work by them for all devices.And we use them multiple purpose.We can produce electricity by using the knowledge of them.



