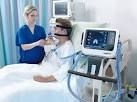
A ventilator (VEN-til-a-tor) is a machine that supports breathing. These machines mainly are used in hospitals. Ventilators:
•Get oxygen into the lungs.
•Remove carbon dioxide from the body. (Carbon dioxide is a waste gas that can be toxic.)
•Help people breathe easier.
•Breathe for people who have lost all ability to breathe on their own.
A ventilator often is used for short periods, such as during surgery when you're under general anesthesia (AN-es-THE-ze-ah). The term "anesthesia" refers to a loss of feeling and awareness. General anesthesia temporarily puts you to sleep.
The medicines used to induce anesthesia can disrupt normal breathing. A ventilator helps make sure that you continue breathing during surgery.
A ventilator also may be used during treatment for a serious lung disease or other condition that affects normal breathing.
Some people may need to use ventilators long term or for the rest of their lives. In these cases, the machines can be used outside of the hospital—in long-term care facilities or at home.
A ventilator doesn't treat a disease or condition. It's used only for life support.