Why more migrants are coming to Europe as winter approaches

AS THEY debated the migrant crisis this summer, often angrily, Europe’s politicians hoped that the winter months would bring some much-needed respite. In previous years, the number of people venturing across the Mediterranean plummeted along with the temperature. In 2014, the number of migrants arriving by boat fell by a third between September and October as the voyage became more dangerous. This October, the opposite happened. A record 218,953 migrants arrived, a 27% increase on September. These migrants must contend with the rougher seas, hypothermia, increased risk of capsize and general misery that such journeys made in winter involve. Why are more migrants now coming to Europe as the dark, cold days approach, not fewer?
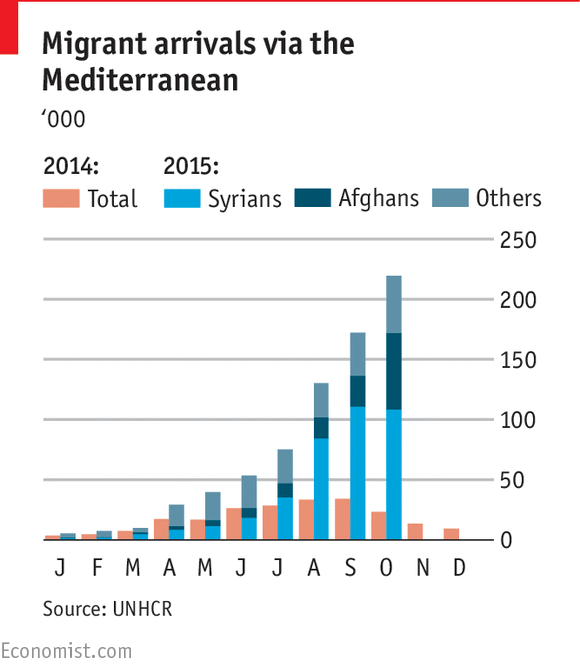
Last year, most migrants arrived in Europe via a dangerous 300km journey from Libya to Lampedusa, an Italian island in the Mediterranean. But winter weather made the trip more arduous and deadly. January's migrant arrivals numbered just 10% of those for the previous September. The same pattern is emerging this year. Rougher seas and a shortage of boats saw arrivals in Italy fall by half last month to just 8,500 arrivals (4% of the total). But migrants now overwhelmingly take the eastern Mediterranean route from western Turkey to the Greek islands. The Aegean Sea is choppy and windy in October, but with journeys as short as 10km—the destination is visible through binoculars—fewer migrants are put off by the rough weather. Even as conditions deteriorate, the sea remains navigable on calm autumn days. On the roughest days, some migrants wait for weather to improve. Others are enticed by a discount from smugglers to risk a voyage.
As winter nears, migrants may be tempted to delay their voyage until the spring. But this year it seems a “now-or-never” attitude has taken hold. Fears abound that Europe will tighten its borders soon, and each week of delay makes the voyage across the Mediterranean more perilous. Moreover, the worsening carnage in Afghanistan has pushed the number of Afghan arrivals in Greece up from 27,500 in September (16% of total arrivals) to 64,000 in October (30%) (see chart). Smugglers are happy to take advantage of despairing migrants. The trafficking business is now worth hundred of millions of dollars and is becoming ever more sophisticated.
A slowdown in migrant arrivals would ease the pressure on European officials. The system that processes asylum claims is creaking. Many migrants face a year-long wait to have their applications processed. Demand for shelter is growing faster than it can be provided, even as temperatures fall. A winter lull would allow authorities to re-design its system before spring, when arrivals could bloom again. If arrival numbers don’t fall, overwhelmed countries may seek to enforce order—as Germany and Sweden both signalled this week. News of harsher policies may filter back to those in Afghanistan and Syria, discouraging them from making the trip. Whether they stay or go, a cruel winter beckons.



